The Placebo Project: An observational study and comprehensive analysis of 134 commonly prescribed homeopathic remedies in India uncovers potential for hepatotoxicity
- PMID: 40725904
- PMCID: PMC12303440
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042560
The Placebo Project: An observational study and comprehensive analysis of 134 commonly prescribed homeopathic remedies in India uncovers potential for hepatotoxicity
Abstract
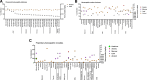
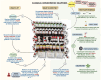
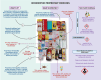
Homeopathy is a popular alternative medical practice globally. However, homeopathic formulations can cause allergies, anaphylaxis, fatal cardiovascular events, kidney injury, liver failure, and death due to their direct and indirect toxicities. This study examined commonly prescribed homeopathic formulations from 3 categories: classical dilutions, mother tinctures, and proprietary products. This cross-sectional study assessed the quality and safety of popular over-the-counter homeopathic formulations. Each remedy underwent complete organic and inorganic content profiling, including heavy metal detection, alcohol quantification, and steroid detection. We analyzed 134 homeopathic remedies and found high alcohol levels, insect and animal parts, carnivorous plants in alcohol, and toxic heavy metals. Classical dilutions had the highest alcohol content (median: 91.02% v/v). Highly diluted formulations of arsenic and mercury had detectable lead levels. Proprietary medicines also showed various potentially toxic bioactive plant compounds, heavy metal contaminants, industrial-grade solvents, and pharmaceutical intermediates, raising concerns about organ toxicity. Homeopathic formulations revealed high ethanol levels and toxic heavy metals like arsenic, lead, mercury, and cadmium. Tinctures and proprietary formulations contained multiple potentially toxic chemicals. Stricter regulatory oversight is needed, and consumers should be aware that the testimonials and anecdotal claims of homeopathic benefits lack scientific validation and can mask potentially harmful effects.
Keywords: AYUSH; herb-induced liver injury; homeopathy; phytochemicals; toxicology.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Homeopathic medicinal products for preventing and treating acute respiratory tract infections in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 9;4(4):CD005974. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005974.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Sep 09;9:CD005974. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005974.pub5. PMID: 29630715 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Homeopathic medicinal products for preventing and treating acute respiratory tract infections in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Sep 9;9(9):CD005974. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005974.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Dec 13;12:CD005974. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005974.pub6. PMID: 30196554 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Homeopathy for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Nov 13;(11):CD009710. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009710.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Sep 04;9:CD009710. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009710.pub3. PMID: 24222383 Updated.
-
Homeopathic medicinal products for preventing and treating acute respiratory tract infections in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Dec 13;12(12):CD005974. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005974.pub6. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36511520 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mukerji N, Ernst E. Why homoeopathy is pseudoscience. Synthese. 2022;200:1–29.
-
- What Is Homeopathy? Explaining pseudoscience, from center for inquiry. https://centerforinquiry.org/learning-resources/explaining-homeopathy/. Accessed December 14, 2024.
-
- Posadzki P, Alotaibi A, Ernst E. Adverse effects of homeopathy: a systematic review of published case reports and case series. Int J Clin Pract. 2012;66:1178–88. - PubMed
-
- Stub T, Kristoffersen AE, Overvåg G, Jong MC, Musial F, Liu J. Adverse effects in homeopathy. A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Explore (NY). 2022;18:114–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

