Postpartum acute intrauterine inversion: A case report
- PMID: 40725912
- PMCID: PMC12303457
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043013
Postpartum acute intrauterine inversion: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: Uterine inversion is a rare and dangerous obstetric emergency, often occurring in the third stage of labor and leading to severe postpartum hemorrhage. It is less common in low-risk pregnant women, yet its prompt management is crucial. This case report fills a gap in the literature by presenting a rare instance in a low-risk young female, offering clinical insights.
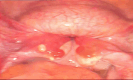
Patient concerns: A low-risk young female had sudden uterine inversion during the third stage of vaginal delivery, with persistent bleeding from the placental site, causing distress and posing an immediate health threat.
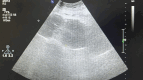
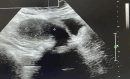
Diagnoses: Physical examination revealed an abnormal uterine position and inability to contract normally, leading to a diagnosis of severe postpartum hemorrhage due to uterine inversion.
Interventions: Immediate medical intervention was carried out to reposition the inverted uterus and control bleeding. After the correction, appropriate measures were taken to ensure stability and prevent complications.
Outcomes: The patient's condition was successfully managed, with the inversion corrected and bleeding stopped. Follow-up showed significant improvement and no long-term complications.
Lessons: This case emphasizes vigilance for rare complications even in low-risk pregnancies and the need for prompt, coordinated intervention. It contributes to knowledge on uterine inversion management for researchers and clinicians.
Keywords: clinical management; low-risk pregnancy; postpartum hemorrhage; third stage of labor; uterine inversion.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Caesarean myomectomy in pregnant women with uterine fibroids.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jan 27;1(1):CD016119. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD016119. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 39868519
-
Breastfeeding or nipple stimulation for reducing postpartum haemorrhage in the third stage of labour.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jan 27;2016(1):CD010845. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010845.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26816300 Free PMC article.
-
Uterine massage for preventing postpartum haemorrhage.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jul 1;2013(7):CD006431. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006431.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23818022 Free PMC article.
-
Cell salvage for the management of postpartum haemorrhage.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 20;12(12):CD016120. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD016120. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39704317
-
Methods for blood loss estimation after vaginal birth.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Sep 13;9(9):CD010980. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010980.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30211952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu H, Bi Z, Hu Q, Liu S, Dong Z, Wang J. Non-puerperal uterine inversion with endometrial polyps in an 11-year-old girl: a case report. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2022;35:188–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous