Epigenetic Histone β-Hydroxybutyrylation Contributes to Renoprotection by β-Hydroxybutyrate in the Dahl Rat
- PMID: 40726393
- PMCID: PMC12444880
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.125.25251
Epigenetic Histone β-Hydroxybutyrylation Contributes to Renoprotection by β-Hydroxybutyrate in the Dahl Rat
Abstract
Background: Previously, we demonstrated that the ketone body, β-hydroxybutyrate, is a potent antihypertensive and reno-protective metabolite in Dahl Salt-Sensitive rats. However, the mechanism by which β-hydroxybutyrate confers these beneficial effects is understudied. Here we focused on determining whether the reno-protective effect of β-hydroxybutyrate is due to its known ability to epigenetically remodel chromatin via histone β-hydroxybutyrylation.
Methods: We used the same animal protocol previously used for the discovery of the reno-protective effect of β-hydroxybutyrate. Briefly, postweaning, male and female Dahl Salt-Sensitive rats were split into 2 groups and supplemented with or without 1,3-butanediol for 6 weeks. At euthanasia, circulating β-hydroxybutyrate was quantitated. Renal homogenates were examined for histone 3 lysine 9 β-hydroxybutyrylation, chromatin occupancy, transcriptomic and proteomic profiles with validations.
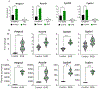
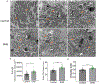
Results: Rats supplemented with 1,3-butanediol had higher circulating β-hydroxybutyrate, renal histone β-hydroxybutyrylation, and significant remodeling of chromatin. Notably, regions of the genome associated with lipid catabolism were predominantly in an open chromatin configuration, leading to active transcription and translation. The most highly upregulated gene actively transcribed and translated was Hmgcs2 (3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA synthase 2), a gene responsible for the biosynthesis of β-hydroxybutyrate in mitochondria. In contrast, regions with more compact chromatin structures contained immune function genes, Ptprc (protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type C) and Lcp1 (lymphocyte cytosolic protein 1), which were suppressed.
Conclusions: These results reveal that renal epigenetic histone β-hydroxybutyrylation is a novel mechanism by which transcriptional regulation of both energy metabolism and immune function occur concomitantly and contribute to renoprotection in the hypertensive Dahl rat.
Keywords: chromatin remodeling; energy metabolism; histones; hypertension; ketones; kidney.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


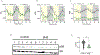

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

