A reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification assay for the rapid detection of goose astrovirus
- PMID: 40726531
- PMCID: PMC12295530
- DOI: 10.30466/vrf.2024.2034344.4346
A reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification assay for the rapid detection of goose astrovirus
Abstract
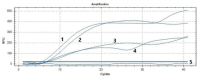
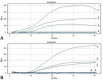
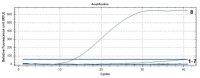
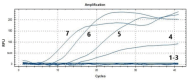
China's burgeoning animal husbandry sector has witnessed a notable expansion in goose farming. Among the various health challenges, a novel goose astrovirus (GoAstV) has emerged as a significant threat to the industry, necessitating prompt detection strategies to mitigate its economic impact. This research introduces a novel detection approach using real-time fluorescence-based reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification (RT-RAA), offering a rapid and reliable method for GoAstV identification. We meticulously designed specific primers and probes, and optimized the RT-RAA reaction conditions. The assay's specificity, sensitivity, repeatability, and clinical efficacy were rigorously assessed. Our method achieves detection within a swift 26-min window at a constant temperature of 39.00 ˚C, boasting a detection threshold as low as 1.19 × 102 copies per μL. Notably, the assay exhibited no cross-reactivity with closely related viruses, including Newcastle disease virus, avian influenza virus H9 subtype, goose circovirus, goose parvovirus, duck Tembusu virus, and avian adenovirus type 4. Validation through testing of 40 clinical samples confirmed a 100% agreement with pre-existing data. The study's outcomes underscore the high specificity, sensitivity, and operational simplicity of the developed RT-RAA assay, positioning it as an ideal candidate for the rapid and on-site detection of GoAstV.
Keywords: Clinical diagnosis; Constant temperature detection; Goose astrovirus; Reverse transcription recombinase-aided amplification.
© 2025 Urmia University. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development and application of a real-time fluorescent RAA assay for H9 subtype avian influenza viruses.Virus Genes. 2025 Aug;61(4):505-511. doi: 10.1007/s11262-025-02167-x. Epub 2025 Jun 11. Virus Genes. 2025. PMID: 40498381
-
A combination of recombinase polymerase amplification with CRISPR technology rapidly detects goose parvovirus with high accuracy and sensitivity.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jun 16;15:1566603. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1566603. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40589866 Free PMC article.
-
Development and application of a dual RT-qPCR assay for differentiating of goose astrovirus genotypes 1 and 2.Res Vet Sci. 2025 Sep;193:105753. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2025.105753. Epub 2025 Jun 7. Res Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40505587
-
The effect of sample site and collection procedure on identification of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 16;12(12):CD014780. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014780. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39679851 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
