Automatic Real-Time Detection and Diagnosis of Liver Tumor with Ultrasound
- PMID: 40726618
- PMCID: PMC12301240
- DOI: 10.2147/JHC.S524311
Automatic Real-Time Detection and Diagnosis of Liver Tumor with Ultrasound
Abstract
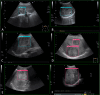
Background/aim: Ultrasonography is the most commonly used screening tool for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the diagnostic performance of ultrasound is highly operator dependent. We aimed to develop deep learning (DL) models to automatically diagnose and detect hepatic lesions in a larger dataset, with HCC as the dominant malignancy.
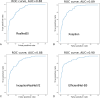
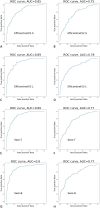
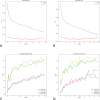
Methods: We enrolled patients diagnosed with hepatic tumors using abdominal ultrasound between January 2002 and December 2020 in a retrospective cohort with a diagnosis of malignant and benign lesions. A total of 1576 patients with 4599 images and 6001 lesions were analyzed. Deep learning models included ResNet50, Xception, Inception Resnet V2, EfficientNet-B5, EfficientNetV2-S, EfficientNetV2-L, Swin-T, and Swin-B for diagnosis and YOLOR for lesion detection. We analyzed the area under the curve (AUC) to determine the diagnostic performance and choose the best model. The mean Average Precision (mAP) score was then evaluated for real-time lesion detection using the area under the precision-recall curve after the average of each category.
Results: The dataset was separated into 1061 in training, 373 in validation, and 142 testing sets. The AUC for ResNet50, Xception, Inception Resnet V2, EfficientNet-B5, EfficientNetV2-S, EfficientNetV2-L, Swin-T, and Swin-B are 0.88, 0.89, 0.88, 0.90, 0.85, 0.89, 0.89, and 0.90, respectively. The mAP scores for detecting and differentiating malignant and benign lesions for YOLOR-W6 and YOLOR-D6 in the validation and testing sets were 0.5134/0.5342 and 0.5410/0.5631.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that DL models can differentiate between benign and malignant lesions with high accuracy on ultrasound images. Simultaneous DL-based lesion detection and classification are also possible using real-time ultrasonography.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; deep learning; diagnosis; liver neoplasms; ultrasonography.
© 2025 Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Chih-Horng Wu, Jin-Chuan Sheu, Pei-Lien Chou, and Hsiao-Ching Nien report a patent TWI810498 issued. The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A deep learning approach to direct immunofluorescence pattern recognition in autoimmune bullous diseases.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jul 16;191(2):261-266. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae142. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38581445
-
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in adults with chronic liver disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 2;9(9):CD013483. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013483.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36053210 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Convolutional Neural Network Model to Predict a Pathologic Fracture in the Proximal Femur Using Abdomen and Pelvis CT Images of Patients With Advanced Cancer.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2023 Nov 1;481(11):2247-2256. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002771. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2023. PMID: 37615504 Free PMC article.
-
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound using SonoVue® (sulphur hexafluoride microbubbles) compared with contrast-enhanced computed tomography and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for the characterisation of focal liver lesions and detection of liver metastases: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2013 Apr;17(16):1-243. doi: 10.3310/hta17160. Health Technol Assess. 2013. PMID: 23611316 Free PMC article.
-
Transabdominal ultrasound and endoscopic ultrasound for diagnosis of gallbladder polyps.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 15;8(8):CD012233. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012233.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30109701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akinyemiju T, Abera S, Ahmed M; Global Burden of Disease Liver Cancer Collaboration. The burden of primary liver cancer and underlying etiologies from 1990 to 2015 at the global, regional, and national level: results from the global burden of disease study 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(12):1683–1691. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3055 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shao -Y-Y, Wang S-Y, Lin S-M, et al. Management consensus guideline for hepatocellular carcinoma: 2020 update on surveillance, diagnosis, and systemic treatment by the Taiwan Liver Cancer Association and the Gastroenterological Society of Taiwan. J Formos Med Assoc. 2021;120(4):1051–1060. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2020.10.031 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

