Engineering a Green Fluorescent Protein-Core-Inspired NIR-Photocage: Exploring meso-GFP-PRPG toward Alzheimer's Disease Therapeutics
- PMID: 40726797
- PMCID: PMC12291143
- DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.5c00027
Engineering a Green Fluorescent Protein-Core-Inspired NIR-Photocage: Exploring meso-GFP-PRPG toward Alzheimer's Disease Therapeutics
Abstract
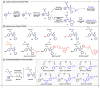
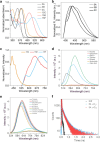
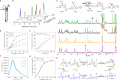
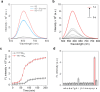
NIR light-activated photocage with inherent protein tagging ability is unprecedented in contemporary photochemistry. Herein, we introduce a series of protein-taggable NIR-photocages derived from green fluorescent protein (GFP) chromophore analogs with spatiotemporal control for releasing the caged bioactive molecules. Through molecular engineering of the GFP chromophoric scaffold, a series of meso-substituted oxazolone-photocages (meso-GFP-PRPG) were judiciously designed and synthesized. These photocages, anchored with electron-donating groups (EDG) and electron-withdrawing groups (EWG), accommodate diverse payloads, including aliphatic carboxylic acids, expanding the possibilities for tailoring their properties and applications. Notably, under anaerobic conditions, irradiation of meso-GFP-PRPG leads to fast and efficient release of caged molecules. Insightful experimental and theoretical investigations revealed that photorelease is predominantly driven by the triplet state photochemistry in anaerobic conditions. The concept's theranostic potential was demonstrated by the conditional release of valproic acid, a neuroprotective agent for Alzheimer's disease (AD) treatment. meso-GFP-PRPG (15E) showed enhanced NIR emission with Aβ oligomers and fibrils (30-37 fold vs ThT) and effectively degraded amyloid fibrils under 640 nm light, offering a promising targeted treatment approach for neurodegenerative disorders.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Green-light responsive fluorescein-based photoremovable protecting group: nanoparticle formulation for controlled release of bioactive molecules with real-time-monitoring ability.J Mater Chem B. 2025 Jun 18;13(24):7172-7180. doi: 10.1039/d5tb00388a. J Mater Chem B. 2025. PMID: 40423568
-
A Novel Design of a Portable Birdcage via Meander Line Antenna (MLA) to Lower Beta Amyloid (Aβ) in Alzheimer's Disease.IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med. 2025 Apr 10;13:158-173. doi: 10.1109/JTEHM.2025.3559693. eCollection 2025. IEEE J Transl Eng Health Med. 2025. PMID: 40657533 Free PMC article.
-
CSF tau and the CSF tau/ABeta ratio for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 22;3(3):CD010803. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010803.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28328043 Free PMC article.
-
Selegiline for Alzheimer's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(1):CD000442. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000442. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. PMID: 12535396
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barltrop J. A., Plant P. J., Schofield P.. Photosensitive Protective Groups. Chem. Commun. 1966:822–823. doi: 10.1039/c19660000822. - DOI
-
- Barltrop J. A., Schofield P.. Photosensitive Protecting Groups. Tetrahedron Lett. 1962;3(16):697–699. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)70935-X. - DOI
-
- Givens R. S., Matuszewski B.. Photochemistry of Phosphate Esters: An Efficient Method for the Generation of Electrophiles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984;106(22):6860–6861. doi: 10.1021/ja00334a075. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
