Potential induction of the relative mRNA expression levels of CYP450 by Zhicaowu-Hezi (Aconiti kusnezoffii radix preparata and Terminalia chebula Retz.)
- PMID: 40727097
- PMCID: PMC12301304
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1573739
Potential induction of the relative mRNA expression levels of CYP450 by Zhicaowu-Hezi (Aconiti kusnezoffii radix preparata and Terminalia chebula Retz.)
Abstract
Background: Processed Aconiti Kusnezoffii Radix (Aconiti kusnezoffii Radix Preparata, Zhicaowu) and Terminalia chebula Retz. (Hezi) are a classic herb pair in Mongolian medicine, where Hezi mitigates Zhicaowu's hepatotoxicity. Despite extensive studies on their detoxification effects, the role of cytochrome P450 (CYP450) modulation remains unclear.
Aim: This study aimed to systematically evaluate the regulatory effects of Zhicaowu and Hezi combination on both enzymatic activity and mRNA expression of CYP450 isoforms (CYP1a2, CYP2b1, CYP2c11, CYP2c13, CYP2d2, CYP2e1, and CYP3a1), and to explore their correlation with hepatoprotective effect.
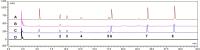
Methods: The effects of Zhicaowu-Hezi formulation on CYP450 enzymes were systematically evaluated through integrated in vivo and in vitro approaches. Rats received 14-day oral administrations of either Zhicaowu, Hezi, or their combinations (1:1, 1:3, 3:1 ratios), followed by comprehensive assessment using: (1) cocktail probe drug assays monitoring seven CYP450 isoforms (CYP1a2, 2b1, 2c11, 2c13, 2d2, 2e1, 3a1) with HPLC quantification methods for substrate detection, (2) RT-qPCR analysis of hepatic CYP450 mRNA expression, and (3) parallel in vitro studies employing rat liver microsomes to verify enzyme activity changes. These pharmacological evaluations were correlated with histopathological and biochemical indices to establish mechanistic relationships between CYP450 modulation and hepatotoxicity attenuation.
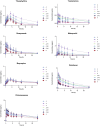
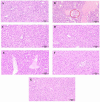
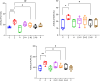
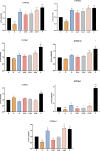
Results: Pathological and biochemical analyses confirmed Hezi's hepatoprotective effects against Zhicaowu-induced toxicity, with the 1:3 Zhicaowu-Hezi combination showing optimal efficacy. In vivo pharmacokinetic studies revealed that Zhicaowu significantly inhibited CYP1a2, CYP2d2, CYP3a1, and CYP2c11 activities, as demonstrated by marked increases in the AUC(0-t), AUC(0-∞)), and Cmax values of their respective probe substrates (theophylline, metoprolol, testosterone, and diclofenac), along with significantly prolonged t1/2 z and reduced CLz/F. It is worth noting that the combined use of Hezi effectively reversed these changes by inducing CYP450, causing significant alterations in the pharmacokinetic parameters of these four substrates. Complementary in vitro studies using liver microsomes consistently showed that Hezi treatment significantly enhanced the metabolic clearance of these four substrates. At the molecular level, RT-qPCR analysis demonstrated that Zhicaowu significantly suppressed hepatic CYP1a2, CYP2d2, CYP3a1, and CYP2c11 mRNA expression, while Hezi co-treatment restored their expression to normal or elevated levels.
Conclusion: Hezi dose-dependently induced CYP450 enzyme activity, reversing Zhicaowu's inhibition of CYP1a2/2d2/3a1/2c11 and markedly improving liver function and histopathology. These results elucidate the scientific basis for toxicity reduction in Zhicaowu-Hezi herb pair through metabolic enzyme regulation, supporting its traditional use. Future studies will focus on toxic alkaloid (e.g., aconitine) pharmacokinetics and their transcriptional regulatory pathways.
Keywords: Aconiti kusnezoffii Radix Preparata; CYP450; Terminalia chebula Retz.; cocktail probe drug method; pharmacokinetics.
Copyright © 2025 Zhu, An, Wang, Guo, Chen, Fang, Wang, Zhang and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Doye S. D., Malur M., Sahu Y., Singh A., Mishra P., Mohamed R. N., et al. (2023). Evaluation and comparison of antibacterial efficacy of different concentrations of Chhattisgarh herbal product-terminalia chebula fruit extract in opposition to enterococcus faecalis: an in vitro study. Food. Sci. Nutr. 12 (2), 1006–1011. 10.1002/fsn3.3814 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- El-Shamarka M. E. A., Aboulthana W. M., Omar N. I., Mahfouz M. M. (2024). Evaluation of the biological efficiency of Terminalia chebula fruit extract against neurochemical changes induced in brain of diabetic rats: an epigenetic study. Inflammopharmacology 32 (2), 1439–1460. 10.1007/s10787-024-01428-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Erdemli M. E., Ekhteiari S. R., Durdagi S., Akgul H., Demirkol M., Aksungur Z., et al. (2018). Biochemical changes induced by grape seed extract and low level laser therapy administration during intraoral wound healing in rat liver: an experimental and in silico study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 36 (4), 993–1008. 10.1080/07391102.2017.1305297 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fan X., Jiang Y., Wang Y., Tan H., Zeng H., Wang Y., et al. (2014). Wuzhi tablet (Schisandra sphenanthera extract) protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by inhibition of CYP-Mediated bioactivation and regulation of NRF2-ARE and p53/p21 pathways. Drug. Metab. Dispos. 42 (12), 1982–1990. 10.1124/dmd.114.059535 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

