Superiority of black-blood computed tomography over conventional computed tomography angiography in the identification of soft plaques: a prospective study
- PMID: 40727329
- PMCID: PMC12290640
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-2024-2989
Superiority of black-blood computed tomography over conventional computed tomography angiography in the identification of soft plaques: a prospective study
Abstract
Background: Carotid computed tomography angiography (CTA) has limited diagnostic value in evaluating the vulnerability of soft plaques. This study compared conventional CTA and black-blood computed tomography (BBCT) in terms of image quality and the ability to diagnose carotid soft plaques.
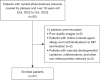
Methods: Patients who underwent carotid CTA and magnetic resonance (MR) vessel wall examination were included in this prospective study. The image quality of plaques was evaluated through objective evaluation [CT values, image noise, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) based on CTA and BBCT] and subjective evaluation. Plaque burden was assessed with the normalized wall index (NWI) in CTA, BBCT, and MR images, as was the remodeling index (RI). The number of soft plaques in CTA, BBCT, and MR images was recorded. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of an NWI higher than 0.56 and an RI higher than 1.0 from CTA and BBCT images in assessing the vulnerability of soft plaques were calculated with MR vessel wall images as a reference standard.
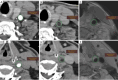
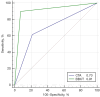
Results: A total of 37 patients comprising 53 soft plaques (25 males and 12 females) were analyzed. The average CT values, SNR, and CNR of soft plaques in BBCT were significantly higher compared to those in CTA (BBCT: 65.38±21.34, 16.31±7.69, 6.47±4.97; CTA: 45.58±14.09, 7.16±3.15, 4.45±2.83; all P values <0.05). The image noise in BBCT was significantly lower than that in CTA (BBCT: 10.73±3.75; CTA: 15.52±6.59; P<0.05), while the subjective image score of BBCT (3.04±0.51) was significantly higher than that of CTA (2.32±0.61) (P<0.001). The sensitivity and specificity of an NWI higher than 0.56 with BBCT were 0.98 and 0.86, respectively, which were superior to those with CTA at 0.83 and 0.57, respectively. Meanwhile, the sensitivity and specificity of an RI higher than 1.0 with BBCT were 0.86 and 0.95, respectively, which were superior to those with CTA at 0.71 and 0.85, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of BBCT in diagnosing vulnerable plaques were 0.90 and 0.93, respectively, while those of CTA were 0.62 and 0.79, respectively. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of BBCT for diagnosing vulnerable plaques was 0.91 (95% CI: 0.803-0.973) while that for CTA was 0.70 (95% CI: 0.559-0.819; P<0.001).
Conclusions: Compared to conventional CTA, BBCT provides improved image quality and diagnostic performance in assessing carotid soft plaques.
Keywords: Vulnerable carotid plaque; black-blood computed tomography (BBCT); computed tomography angiography (CTA); magnetic resonance (MR); vessel wall.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://qims.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/qims-2024-2989/coif). T.Z. received funding from the Clinical Medical Science and Technology Innovation Development Program of Jinan (Nos. 202134053 and 202430066), and the Science and Technology Development Program of Jinan Municipal Health Commission (No. 2022-2-37). M.Z. received funding from the Clinical Medical Science and Technology Innovation Development Program of Jinan (No. 202225061). M.L. received funding from Medical and Health Technology Development Program Project of Shandong Province (No. 202109011085). Z.M. is an employee of Canon Medical System. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures





References
-
- Stary HC, Chandler AB, Glagov S, Guyton JR, Insull W, Jr, Rosenfeld ME, Schaffer SA, Schwartz CJ, Wagner WD, Wissler RW. A definition of initial, fatty streak, and intermediate lesions of atherosclerosis. A report from the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on Arteriosclerosis, American Heart Association. Circulation 1994;89:2462-78. 10.1161/01.cir.89.5.2462 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
