Effect and Safety of Finerenone in Patients with IgA Nephropathy
- PMID: 40727456
- PMCID: PMC12302221
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S531236
Effect and Safety of Finerenone in Patients with IgA Nephropathy
Abstract
Purpose: The study aimed to retrospectively evaluate the efficacy and safety of finerenone in patients diagnosed with IgA nephropathy.
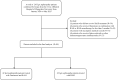
Methods: 42 IgA nephropathy patients treated with finerenone combined with renin-angiotensin system inhibitor (RASI) and 42 patients who received RASI monotherapy were included in this study. The follow-up duration was 3 months. The efficacy and safety of finerenone were assessed based on key parameters, including urine protein creatinine ratio (UPCR), estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), serum creatinine, serum albumin, hematuria, and serum potassium at 1 and 3 months after treatment initiation.
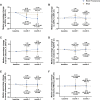
Results: This study demonstrated that finerenone combined with RASI significantly reduced proteinuria in IgA nephropathy patients. Two-way repeated measures ANOVA revealed a significant time * treatment interaction (P = 0.032), and subsequent one-way repeated measures ANOVA showed a marked decline in log-transformed UPCR over time in the combination group (P < 0.001) but not in the monotherapy group (P = 0.187). Correspondingly, the combination group achieved a 27.29% reduction in UPCR at one month (95% CI: 13.47-39.68%, P = 0.017) and a 34.17% reduction at three months (95% CI: 21.84-52.75%, P < 0.001) compared to baseline, whereas RASI monotherapy failed to show any significant proteinuria-reduction effects. Notably, the antiproteinuric effect was consistent across subgroups. Serum potassium and creatinine levels remained stable, and no adverse events related to hyperkalemia were observed.
Conclusion: The retrospective evaluation suggests that finerenone combined with RASI effectively reduced proteinuria in IgA nephropathy patients, underscoring its potential as a viable treatment option for this patient population.
Keywords: IgA nephropathy; finerenone; renin–angiotensin system inhibitor; urine protein creatinine ratio.
© 2025 Guo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in this work.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

