Recent advances and perspectives of MicroNeedles for biomedical applications
- PMID: 40727662
- PMCID: PMC12290160
- DOI: 10.1007/s12551-025-01317-7
Recent advances and perspectives of MicroNeedles for biomedical applications
Abstract
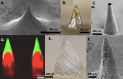
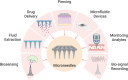
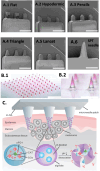
Microneedles (MN) technology has emerged as a transformative tool within the biomedical field, offering innovative solutions to challenges in drug delivery, diagnostics, and therapeutic applications. This review article provides an in-depth exploration of the diverse perspectives and applications of MNs, shedding light on their pivotal role in shaping the future of biomedical research and clinical practice. It begins by elucidating the fundamental principles of MNs: design, fabrication techniques, and materials, highlighting their capacity for minimally invasive access to the skin and underlying tissues. These attributes have driven advancements in transdermal drug delivery, facilitating precise and controlled administration of therapeutics, vaccines, and biologics, thus improving patient compliance and treatment outcomes. Furthermore, this review investigates the growing range of applications for MNs, including biomarker extraction, interstitial fluid (ISF) analysis, and continuous glucose monitoring. MNs enable real-time and minimally invasive monitoring of biochemical markers and have the potential to revolutionize disease diagnostics, personalized medicine, and wellness monitoring. Their compatibility with microfluidic systems further enhances their potential for point-of-care testing. This review serves as a comprehensive guide, highlighting the breadth of opportunities and challenges in leveraging MNs to improve healthcare outcomes and emphasizing the need for continued research and development in this dynamic field.
Keywords: Drug delivery; Fluid Extraction; MicroNeedles; Microfabrication; Microfluidic Devices.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Alfalasi H et al (2025) Hydrogel-based microneedles for the delivery of catalase protein. Int J Pharm. 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125387 - PubMed
-
- Amani H et al (2021) Microneedles for painless transdermal immunotherapeutic applications. J Control Release. 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.12.019 - PubMed
-
- Ameri M et al (2010) Parathyroid hormone PTH(1–34) formulation that enables uniform coating on a novel transdermal microprojection delivery system. Pharm Res. 10.1007/S11095-009-0019-8 - PubMed
-
- Angkawinitwong U et al (2020) A Novel Transdermal Protein Delivery Strategy via Electrohydrodynamic Coating of PLGA Microparticles onto Microneedles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 10.1021/acsami.9b22425 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

