Acid Phosphatase Produced by in Solid Fermentation Using Millet
- PMID: 40727733
- PMCID: PMC12290674
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c10512
Acid Phosphatase Produced by in Solid Fermentation Using Millet
Abstract
The absorption of organic phosphorus from the environment and its efficient use requires the action of a large class of enzymes called acid phosphatases. Fungi can convert insoluble phosphorus into soluble forms during the acidification and chelation stages or through hydrolysis mediated by phosphatase enzymes. These enzymes are obtained from plants, animal cells, and microorganisms. Acid phosphatases (AcPases) have their optimum pH of action being less than 6.00. This study evaluated the production and extraction of acid phosphatases using solid fermentation (FES) with supported in millet. Preliminary tests were fundamental in analyzing the enzyme production potential of the strain, where the best results were for millet. Using a Central Composite Design (CCD), it was possible to develop equations for responses to acid phosphatase activity (U/mL) and dry biomass (g/L) using the variables: millet mass, inoculum concentration, and moisture. The best results were for solid fermentation, using the millet substrate with cultivation in sterile distilled water and extraction with Tween 80, where there was a growth of biomass and enzymatic activity, whose optimized final values were 9.27 ± 0.53 g/L and 36.09 ± 0.61 U/mL, respectively, after 9 days of solid fermentation.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures



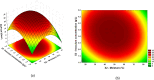
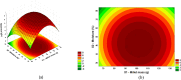



References
-
- Bouras H., Mamassi A., Devkota K. P., Choukr-Allah R., Bouazzama B.. Integrated effect of saline water irrigation and phosphorus fertilization practices on wheat (Triticum aestivum) growth, productivity, nutrient content and soil proprieties under dryland farming. Plant Stress. 2023;10:100295. doi: 10.1016/j.stress.2023.100295. - DOI
-
- Zhang J., Feng L., Ouyang Y., Hu R., Xu H., Wang J.. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and fungi in relation to phosphorus availability under different land uses for some latosols from Guangdong, China. Catena. 2020;195:104686. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104686. - DOI
-
- Zaman U., Khan S. U., Hendi A. A., Rehman K., Badshah S., Refat M. S., Alsuhaibani A. M., Ullah K. K., Wahab A.. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of novel acid phosphatase isolated and purified from Carthamus oxyacantha seedlings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023;224:20–31. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.12.025. - DOI - PubMed
-
- da Silva G., Ramos L. F. C., dos Santos Seckler H. F., Gomes J. M., Cortines I. R., Ramos C., Anobom E. D., Machado D. M. A., Oliveira P.. Biochemical characterization of digestive membrane associated alkaline phosphatase from the velvet bean caterpillar Anticarsia gemmatalis . Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2019;102:e21591. doi: 10.1002/arch.21591. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
