Transcriptome Analysis of Triple-Negative HCC1937 and MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells Treated with Revealed the Regulation of Migration and Invasion via the Downregulation of the Genes JAK2, ROCK1 and ROCK2
- PMID: 40727786
- PMCID: PMC12290928
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c05895
Transcriptome Analysis of Triple-Negative HCC1937 and MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells Treated with Revealed the Regulation of Migration and Invasion via the Downregulation of the Genes JAK2, ROCK1 and ROCK2
Abstract
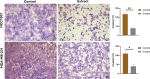
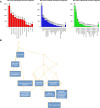
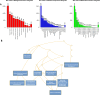
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a type of breast cancer with high mortality due to aggressive tumor behavior and limited treatment options. Natural products have been studied for their potential as alternatives to combine with cancer drugs to improve treatment efficacy. Plant phytoconstituents can regulate cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, invasion, angiogenesis, and migration. has been used in traditional medicine; it contains flavonoids, phenols, alkaloids, glycosides, bufadienolides, and tannins, among others. In the present investigation, we evaluated the effects of aqueous extract and the underlying molecular mechanisms in two breast cancer cell lines, HCC1937 and MDA-MB-231, with a focus on cellular migration. The cytotoxic activity results revealed that HCC1937 cells are more sensitive to aqueous extracts than are MDA-MB-231 cells. Compared with that of 48 h-treated MDA-MB-231 cells, cell migration was affected in HCC1937 cells after 24 h of treatment. The extract had greater anti-invasion effects on HCC1937 cells (37.7%, p < 0.01) than on MDA-MB-231 cells (47%, p < 0.05). An RNA-seq assay revealed 1850 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in HCC1937 cells versus 1534 in MDA-MB-231 cells. WebGestalt analysis revealed the downregulation of genes involved in cell-cell adhesion, ruffle organization, and cell-substrate junctions, with more downregulated genes in HCC1937 cells. The downregulated genes analyzed with KOBAS-i were associated with MAPK signaling, focal adhesion, PI3K-Akt signaling, regulation of the actin cytoskeleton, and the ECM-receptor interaction pathway. In addition, IPA network analysis revealed that the RHO GTPase cycle, RHOA signaling, JAK/STAT signaling, actin cytoskeleton signaling and Integrin signaling pathways were inhibited. The data from the docking study indicated the binding potential of quercetin-3-O-arabinoside, kaempferol, quercetin, and apigenin with the JAK2, ROCK1, ROCK2, and PIK3CA proteins. Thus, our results demonstrate that inhibits the proliferation and invasion of TNBC cells by targeting genes involved in these important processes; thus, has the potential to be used in combination with chemotherapeutic drugs for cancer treatment.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Zhuidu Formula suppresses the migratory and invasive properties of triple-negative breast cancer cells via dual signaling pathways of RhoA/ROCK and CDC42/MRCK.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Oct 28;315:116644. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116644. Epub 2023 May 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37196814
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alteration of m6A Methylation in Breast Cancer Cells by Kalanchoe pinnata Aqueous Extract.Molecules. 2025 Jun 18;30(12):2634. doi: 10.3390/molecules30122634. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40572597 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding mechanisms of Polygonatum sibiricum-derived exosome-like nanoparticles against breast cancer through an integrated metabolomics and network pharmacology analysis.Front Chem. 2025 Jun 6;13:1559758. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1559758. eCollection 2025. Front Chem. 2025. PMID: 40547857 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Quazi M. A., Tatiya A. U., Khurshid M.. et al. THE MIRACLE PLANT (KALANCHOE PINNATA): A PHYTOCHEMICAL AND PHARMACOLOGICAL REVIEW. Int. J. Res. Ayurveda Pharm. 2011;2:1478–1482.
-
- Rajsekhar P., Bharani R., Ramachandran M.. et al. The “Wonder Plant” Kalanchoe pinnata (Linn.) Pers.: A Review. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2016;6:151–158. doi: 10.7324/JAPS.2016.60326. - DOI
-
- Allorge-Boiteau, L. Madagascar centre de speciation et d’origine du genre Kalanchoe (Crassulaceae). In Biogéographie de Madagascar; Lourenç o, W. R. , Ed.; ORSTOM, 1996; pp 137–145.
-
- Machinski I., Andrade E. A., Schaffka V. M., de Almeida V. P., Santos A., Bueno D., Perera W. H., Pereira R. P., Manfron J., Miyoshi E.. et al. Exploring the Pharmacognostical and Phytochemical Profiles of Aqueous Extracts of Kalanchoe . Chem. Biodiversity. 2024;21:e202400660. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202400660. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
