An injectable calcium sulfate-monetite biphasic cement for the treatment of critical-sized calvarial defects
- PMID: 40728601
- PMCID: PMC12307452
- DOI: 10.1007/s10856-025-06911-5
An injectable calcium sulfate-monetite biphasic cement for the treatment of critical-sized calvarial defects
Abstract
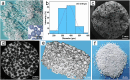
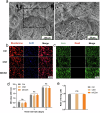
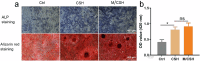
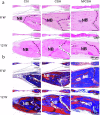
The critical bone defect is a common clinical challenge worldwide, characterized by long recovery times, a substantial risk of infection, and high disability rates. There remains a significant demand for synthetic bone-repairing materials to address this issue. In this study, porous monetite was synthesized through the reaction between monocalcium phosphate monohydrate and β-tricalcium phosphate, using paraffin microspheres as pore-forming agents. An injectable biphasic cement was then developed by blending the monetite granules with hemihydrate calcium sulfate, designed for minimally invasive surgical applications. The cement demonstrated excellent biocompatibility and osteogenic properties in vitro. Furthermore, in vivo studies confirmed the cement's superior bone repair capabilities, indicating its promising potential for the treatment of critical bone defects.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standards. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Guo W, Xu H, Liu D, Dong L, Liang T, Li B, et al. 3D-Printed lattice-inspired composites for bone reconstruction. J Mater Chem B. 2023;11:7353–63. 10.1039/d3tb01053h - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

