Serum Levels of IL-21 and IL-22 in Breast Cancer Patients-A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 40729006
- PMCID: PMC12293384
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb47070537
Serum Levels of IL-21 and IL-22 in Breast Cancer Patients-A Preliminary Study
Abstract
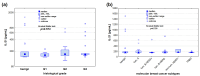
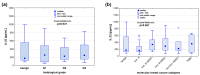
Breast cancer is one of the most commonly diagnosed malignant tumours in women worldwide. Although modern medicine has led to advanced diagnostic methods and therapies that allow for increasingly effective treatment, the mechanisms underlying breast cancer development and progression remain the subject of intensive research. In the pathogenesis of this cancer, significant importance is attributed to interactions between tumour cells and the tumour microenvironment, in which soluble immune system mediators-cytokines-play a key role, including IL-21 and IL-22. These interleukins, by modulating the immune response, can both promote and inhibit tumour progression, and analysing their concentrations may prove helpful in diagnosis, disease progression prognosis, and the development of new therapies, including immunotherapy. The aim of this study was to determine the concentrations of IL-21 and IL-22 in a group of patients with invasive cancer, depending on the biological type of the tumour and its malignancy grade. The study involved 60 women with breast cancer and 20 women with benign breast lesions, and the analysis of IL-21 and IL-22 protein concentrations was performed using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method. The analysis shows that the concentrations of IL-21 and IL-22 do not differ significantly depending on the malignancy grade of the tumour. However, a statistically significant negative correlation between the concentrations of IL-21 and IL-22 was observed exclusively in the group of patients with benign breast lesions. Due to the high heterogeneity of breast cancers, further research with a larger study group is necessary to better understand these parameters and possibly apply them clinically in patients with breast cancer.
Keywords: IL-21; IL-22; breast cancer; tumour microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Intraoperative frozen section analysis for the diagnosis of early stage ovarian cancer in suspicious pelvic masses.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 1;3(3):CD010360. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010360.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26930463 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L., Laversanne M., Soerjomataram I., Jemal A., Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Harbeck N., Gnant M. Breast cancer. Lancet. 2017;389:1134–1150. - PubMed
-
- Katsura C., Ogunmwonyi I., Kankam H.K., Saha S. Breast cancer: Presentation, investigation and management. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2022;83:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Nalbant A. IL-17, IL-21, and IL-22 Cytokines of T Helper 17 Cells in Cancer. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2019;39:56–60. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

