Challenges in Assessing Aphasia in Congenital Blind Patients: A Case Report
- PMID: 40729172
- PMCID: PMC12225366
- DOI: 10.3390/reports6040049
Challenges in Assessing Aphasia in Congenital Blind Patients: A Case Report
Abstract
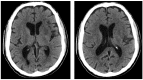
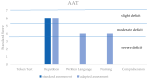
This case report focuses on assessing aphasia in a congenitally blind patient with an ischemic lesion using the Aachener Aphasia Test. The method involved adapting existing assessment tools to the patient, integrating Braille as an accessible technology, and incorporating the patient's family for emotional support and for the identification of patient-specific communication strategies. The assessment revealed patient strengths in areas such as articulation, prosody, and repetition skills, but also exposed challenges in semantic and syntactic structures. However, the unavailability to assess and score naming and comprehension limited a full assessment of the patient's language abilities. The findings underscore the need for flexible, tailored assessment strategies and collaborative approaches involving healthcare professionals and families. Moreover, it suggests a considerable research gap and a need for standard tools to assess blind patients with aphasia comprehensively. This case report contributes to the limited knowledge of assessing aphasia in blind individuals and calls for further research in this area to refine and expand the available tools and strategies.
Keywords: blindness; broca aphasia; communication aids for disabled; health communication; sensory aids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cypriot Healthcare Professionals' Knowledge and Skills When Interacting With Patients With Aphasia in Clinical Settings.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025 Jul-Aug;60(4):e70089. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.70089. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025. PMID: 40608388 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions to improve safe and effective medicines use by consumers: an overview of systematic reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 29;2014(4):CD007768. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007768.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24777444 Free PMC article.
-
Music interventions for acquired brain injury.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 20;1(1):CD006787. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006787.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28103638 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Neonatal Nurses' Understanding of the Factors That Enhance and Hinder Early Communication Between Preterm Infants and Their Parents: A Narrative Inquiry Study.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025 Jul-Aug;60(4):e70093. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.70093. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025. PMID: 40653954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ghoreyshi Z., Nilipour R., Bayat N., Nejad S.S., Mehrpour M., Azimi T. The Incidence of Aphasia, Cognitive Deficits, Apraxia, Dysarthria, and Dysphagia in Acute Post Stroke Persian Speaking Adults. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022;74:5685–5695. doi: 10.1007/s12070-021-03006-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
