Navigating Complexity in Pediatric NMOSD: Unusual Symptoms and Adverse Reactions: A Case Report
- PMID: 40729219
- PMCID: PMC12199969
- DOI: 10.3390/reports8010006
Navigating Complexity in Pediatric NMOSD: Unusual Symptoms and Adverse Reactions: A Case Report
Abstract
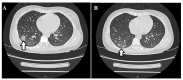
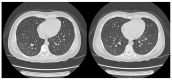
Background and Clinical Significance: Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) is a rare autoimmune demyelinating disorder of the central nervous system, characterized by the presence of aquaporin-4 (AQP4) antibodies and a high relapse rate. We provide information about the diagnosis, unusual symptoms, and treatment of a paediatric patient with NMOSD. Case Presentation: A 14-year-old girl was hospitalized for weakness and paraesthesia of the lower limbs (LL). The patient underwent detailed investigations and was diagnosed with NMOSD and cryptogenic organizing pneumonia. Initial treatment with methylprednisolone and prednisone yielded a favourable response. Therapy with mycophenolate was initiated. However, the patient experienced two more relapses, prompting the use of rituximab therapy with a favourable outcome and a two-year relapse-free follow-up period. Conclusions: Patients with NMOSD may have multisystemic inflammation, including organs outside the central nervous system. Our case report highlights a case of NMOSD, pulmonary involvement, and unusual adverse reactions to rituximab.
Keywords: AQP4 antibodies; NMOSD; demyelinating disorder; paediatric.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Uncommon Non-MS Demyelinating Disorders of the Central Nervous System.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):45. doi: 10.1007/s11910-025-01432-8. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40591029 Review.
-
Ravulizumab is Effective and Safe for Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder Patients in Various Clinical Settings: A Single-Center Case Series with Concomitant Use of Rituximab.Cureus. 2025 May 23;17(5):e84703. doi: 10.7759/cureus.84703. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40551924 Free PMC article.
-
Dual BLyS/APRIL targeted therapy with telitacicept in rituximab-refractory SLE-associated neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: a case report.Front Immunol. 2025 May 26;16:1602800. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1602800. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40491913 Free PMC article.
-
A Chinese girl with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder coexisting with primary Sjogren's syndrome: a case report and literature review.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 8;16:1559825. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1559825. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40698091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AQP4-IgG-positive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder and temporally detected neoplasms: case report and systematic review.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2022 Dec;68:104212. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2022.104212. Epub 2022 Oct 4. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2022. PMID: 36242805
References
-
- Wingerchuk D.M., Banwell B., Bennett J.L., Cabre P., Carroll W., Chitnis T., de Seze J., Fujihara K., Greenberg B., Jacob A., et al. International Consensus Diagnostic Criteria for Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders. Neurology. 2015;865:177–189. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001729. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kümpfel T., Giglhuber K., Aktas O., Ayzenberg I., Bellmann-Strobl J., Häußler V., Havla J., Hellwig K., Hümmert M.W., Jarius S., et al. Update on the diagnosis and treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD)—Revised recommendations of the Neuromyelitis Optica Study Group (NEMOS). Part II: Attack therapy and long-term management. J. Neurol. 2024;271:141–176. doi: 10.1007/s00415-023-11910-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
