Cerebrovascular Thrombosis in Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis: A Case Report
- PMID: 40729235
- PMCID: PMC12199963
- DOI: 10.3390/reports8010022
Cerebrovascular Thrombosis in Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis: A Case Report
Abstract
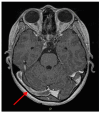
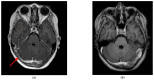
Background and Clinical Significance: Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a severe extra-intestinal manifestation that can complicate the course of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Among pediatric patients, cerebral thrombosis (CT) is the most common form of VTE associated with IBD. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) remains the gold standard for diagnosing cerebral venous thrombosis, allowing visualization of flow absence and intraluminal thrombus. Prompt initiation of treatment with low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) is crucial to prevent complications. Follow-up imaging is essential to evaluate venous recanalization and guide therapy duration. However, data on cerebral thrombosis in pediatric patient with IBD remain scarce. Case Presentation: We report the case of a 12-year-old boy with a known history of ulcerative colitis who presented to the emergency room (ER) with a two-day history of headache and vomiting. One month prior to the ER visit, he experienced an IBD flare confirmed through clinical, biochemical, and endoscopic evaluation and was subsequently started on oral corticosteroids. Neurological examination was unremarkable; however, given the persistence of severe headache, a brain MRI was performed, leading to a diagnosis of cerebral venous thrombosis. Anticoagulation therapy with LMWH was initiated immediately. Follow-up imaging with contrast-enhanced MR venography four months later revealed partial resolution of the thrombosis. The patient continued long-term anticoagulation therapy for a total duration of 12 months. Conclusions: Cerebral venous thrombosis is a serious complication of IBD, particularly in pediatric patients. Clinicians should consider this diagnosis in any child with IBD presenting with persistent headache, even in the absence of focal neurological signs. Early diagnosis and prompt anticoagulation therapy are key to improving outcomes in these patients.
Keywords: children; inflammatory bowel disease; thrombosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Home versus in-patient treatment for deep vein thrombosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 9;1(1):CD003076. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003076.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29315455 Free PMC article.
-
Pentasaccharides for the prevention of venous thromboembolism.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 31;10(10):CD005134. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005134.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27797404 Free PMC article.
-
Patient education interventions for the management of inflammatory bowel disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 May 4;5(5):CD013854. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013854.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37172140 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions for the management of abdominal pain in Crohn's disease and inflammatory bowel disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Nov 29;11(11):CD013531. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013531.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34844288 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of testing for cancer on cancer- and venous thromboembolism (VTE)-related mortality and morbidity in people with unprovoked VTE.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 23;8(8):CD010837. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010837.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Nov 08;11:CD010837. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010837.pub4. PMID: 28832905 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Ando K., Fujiya M., Nomura Y., Inaba Y., Sugiyama Y., Kobayashi Y., Iwama T., Ijiri M., Takahashi K., Ueno N., et al. The Incidence and Risk Factors of Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Prospective Multicenter Cohort Study. Digestion. 2019;100:229–237. doi: 10.1159/000495289. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Turner D., Ruemmele F.M., Orlanski-Meyer E., Griffiths A.M., de Carpi J.M., Bronsky J., Veres G., Aloi M., Strisciuglio C., Braegger C.P., et al. Management of Paediatric Ulcerative Colitis, Part 2: Acute Severe Colitis—An Evidence-Based Consensus Guideline From the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organization and the European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018;67:292–310. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000002036. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Saposnik G., Barinagarrementeria F., Brown R.D., Jr., Bushnell C.D., Cucchiara B., Cushman M., deVeber G., Ferro J.M., Tsai F.Y., American Heart Association Stroke C., et al. Diagnosis and management of cerebral venous thrombosis: A statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2011;42:1158–1192. doi: 10.1161/STR.0b013e31820a8364. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
