Type I Diabetes-A Rare Adverse Event Described in Patients Receiving Immunotherapy Versus a Side Effect from SARS-CoV-2 Infection
- PMID: 40729244
- PMCID: PMC12199958
- DOI: 10.3390/reports8010031
Type I Diabetes-A Rare Adverse Event Described in Patients Receiving Immunotherapy Versus a Side Effect from SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Abstract
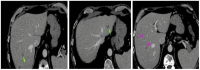
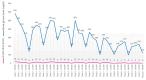
Background and Clinical Significance: Lung cancer, a leading cause of global cancer diagnoses, maintains the highest mortality risk despite advances in treatment. Immunotherapy agents, such as anti-programmed death-1/programmed death ligand-1 (PD-1/PD-L1), have revolutionized care for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, the success is tempered by the emergence of immune-mediated adverse reactions, including the rare onset of type I diabetes. The incidence of diabetes mellitus increased during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. While there are several cases of new-onset diabetes after COVID-19 and COVID-19 vaccination, no case of new-onset type 1 diabetes after COVID-19 was described in an immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI)-treated patient. Case Presentation: A 57-year-old male with stage IV NSCLC (brain and liver metastases) who had been treated with nivolumab for 4 years appeared positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection at a routine check. After two weeks, he was admitted to our clinic with severe fatigue, hyperglycemia, hyponatremia, and hyperkalemia. HbA1c level was normal and serum peptide C was undetectable. Nivolumab treatment was ceased, and the patient became fully dependent on basal-bolus insulin. After 3 months, the patient showed a complete imagistic remission. Conclusions: The case presented significant challenges due to the unclear etiology of newly onset diabetes and the uncommon age at which type 1 diabetes is developed. The outcome suggests that anti-PD-1 and SARS-CoV-2 infection can act synergistically.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2 pandemic; adverse effect; immunotherapy; lung cancer; type I diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
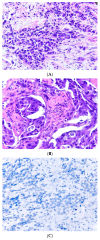
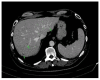
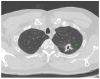
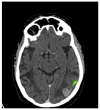


References
-
- Garon E.B., Hellmann M.D., Rizvi N.A., Carcereny E., Leighl N.B., Ahn M.-J., Eder J.P., Balmanoukian A.S., Aggarwal C., Horn L., et al. Five-Year Overall Survival for Patients With Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treated With Pembrolizumab: Results From the Phase I KEYNOTE-001 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019;37:2518–2527. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00934. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
