A rare case report of neuro-brucellosis with concurrence of depression, visual impairment, bilateral sensorineural hearing loss, and paraplegia
- PMID: 40729377
- PMCID: PMC12331110
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012824
A rare case report of neuro-brucellosis with concurrence of depression, visual impairment, bilateral sensorineural hearing loss, and paraplegia
Abstract
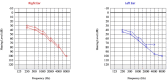
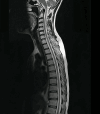
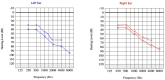
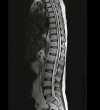
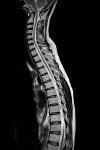
Neurobrucellosis is a rare manifestation of brucella infection, which would be life-threatening and result in multiple disabilities. Brucellosis commonly manifests with fever, arthralgia, and myalgia. Moreover, most patients with Neurobrucellosis present with significant lesions in the brain, spinal cord, or vertebral column; some cases show no lesions in their magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The present case is a 32-year-old rural man with suspicious contact with animals at his work who was presented with ataxia, paraplegia, and urine-fecal incontinence without typical symptoms of brucellosis. Broad-spectrum diagnostic methods for neurobrucellosis were employed, including the Wright and 2-mercaptoethanol (2-ME) tests on plasma and brain, as well as spinal MRI. However, no significant pathologies were found in the brain or spinal imaging that could explain the patient's clinical condition, and the Wright and 2-ME tests were negative. Also, despite a comprehensive approach to different viral, bacterial, autoimmune, systemic, metabolic, and organic etiologies, the symptoms of the patient got worse, and he experienced depression, sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL), and visual impairment in the following months. Eventually, the patient's cerebrospinal fluid specimen Wright & 2-ME tests became positive, and a standard antibiotic regimen, including doxycycline, rifampin, and ceftriaxone, was administered for several months. In his last follow-up two years later, all neurological and psychological issues had disappeared except mild ataxia and hearing impairment. Hence, the prozone phenomenon should be considered in the false-negative Wright tests in endemic regions for brucellosis.
Copyright: © 2025 Pourmontaseri et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Intraoperative frozen section analysis for the diagnosis of early stage ovarian cancer in suspicious pelvic masses.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 1;3(3):CD010360. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010360.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26930463 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Severe Relapsing Hailey-Hailey Disease Displaying a Durable Complete Response to Hydroxyurea.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2024 Nov;32(3):168-169. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2024. PMID: 40654217
References
-
- Pappas G, Akritidis N, Bosilkovski M, Tsianos E. Brucellosis. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(22):2325–36. - PubMed
-
- Corbel MJ. Brucellosis in humans and animals. World Health Organization; 2006.
-
- Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Stackebrandt E, Schleifer K-H. The prokaryotes: a handbook on the biology of bacteria. Springer; 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

