The Medical Impact of Hepatitis D Virus Infection in Natives and Immigrants: The Italian Paradigm
- PMID: 40729522
- PMCID: PMC12306849
- DOI: 10.1111/liv.70242
The Medical Impact of Hepatitis D Virus Infection in Natives and Immigrants: The Italian Paradigm
Abstract
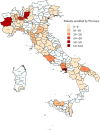
Background and aim: Ongoing migratory flows are reconstituting the hepatitis D virus (HDV) reservoir in Italy. We aimed to characterise the current clinical and virologic features of HDV infection in both native Italians and migrants.
Methods: We enrolled 515 hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)-positive patients with detectable anti-HDV antibodies from 32 Italian centres between August 2022 and July 2024; all patients underwent centralised virologic assessment.
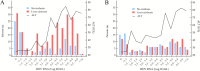
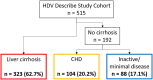
Results: Overall, 432 out of 515 (83.9%) patients were HDV-RNA-positive (4.39, 1.30-5.82 Log IU/mL; 99.0% HDV genotype-1). HDV-RNA levels correlated with ALT (rs = 0575, 0.514-0.630) and hepatitis B core-related antigen (rs = 0.521, 0.455-0.581). Native Italians (n = 317; 61.6%) were older than migrants (n = 198; 38.4%) (median age: 60, 55-65 vs. 46, 39-54 years; p < 0.001) and were more frequently male (68.1% vs. 49.5%; p < 0.001), with a higher prevalence of liver cirrhosis (70.3% vs. 50.5%; p < 0.001) and hepatocellular carcinoma (14.8% vs. 0.5%; p < 0.001). Among Italians, 223 (70.3%) had liver cirrhosis, 46 (14.5%) had chronic hepatitis D (CHD) without cirrhosis and 48 (15.1%) exhibited inactive/minimal disease with low viremia (≤ 3 Log IU/mL). Among migrants, 100 (50.5%) had liver cirrhosis, 58 (29.3%) had CHD and 40 (20.2%) showed inactive/minimal disease with low viremia (≤ 3 Log IU/mL).
Conclusions: The current clinical landscape of chronic HDV infections in Italy is heterogeneous, changing the perspective of CHD as uniformly severe; although cirrhosis remains common, a substantial proportion of both native Italians and migrants present with milder forms of disease.
Keywords: HDV; HDV‐RNA; chronic hepatitis D; cirrhosis; epidemiology.
© 2025 The Author(s). Liver International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
G.P.C. reports grants from Fujirebio Diagnostics AB; A.L. reports consulting and/or speaker fees from Gilead Sciences. M.V. reports consulting and/or speaking fees from Gilead Sciences, and Ipsen. S.F. reports consulting and/or speaking fees from Gilead Sciences, Roche and Alfasigma. All other authors report no potential conflicts.
Figures
References
-
- Rizzetto M., Hamid S., and Negro F., “The Changing Context of Hepatitis D,” Journal of Hepatology 74, no. 5 (2021): 1200–1211. - PubMed
-
- Rizzetto M., “The Delta Agent,” Hepatology 3, no. 5 (1983): 729–737. - PubMed
-
- Rosina F., Conoscitore P., Cuppone R., et al., “Changing Pattern of Chronic Hepatitis D in Southern Europe,” Gastroenterology 117, no. 1 (1999): 161–166. - PubMed
-
- Niro G. A., Smedile A., Ippolito A. M., et al., “Outcome of Chronic Delta Hepatitis in Italy: A Long‐Term Cohort Study,” Journal of Hepatology 53, no. 5 (2010): 834–840. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

