Evaluating the accuracy of artificial intelligence-powered chest X-ray diagnosis for paediatric pulmonary tuberculosis (EVAL-PAEDTBAID): Study protocol for a multi-centre diagnostic accuracy study
- PMID: 40730400
- PMCID: PMC12306472
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2025-105881
Evaluating the accuracy of artificial intelligence-powered chest X-ray diagnosis for paediatric pulmonary tuberculosis (EVAL-PAEDTBAID): Study protocol for a multi-centre diagnostic accuracy study
Abstract
Introduction: Diagnosing pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) in children is challenging owing to paucibacillary disease, non-specific symptoms and signs and challenges in microbiological confirmation. Chest X-ray (CXR) interpretation is fundamental for diagnosis and classifying disease as severe or non-severe. In adults with PTB, there is substantial evidence showing the usefulness of artificial intelligence (AI) in CXR interpretation, but very limited data exist in children.
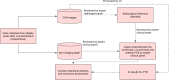
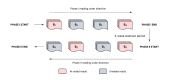
Methods and analysis: A prospective two-stage study of children with presumed PTB in three sites (one in South Africa and two in Pakistan) will be conducted. In stage I, eligible children will be enrolled and comprehensively investigated for PTB. A CXR radiological reference standard (RRS) will be established by an expert panel of blinded radiologists. CXRs will be classified into those with findings consistent with PTB or not based on RRS. Cases will be classified as confirmed, unconfirmed or unlikely PTB according to National Institutes of Health definitions. Data from 300 confirmed and unconfirmed PTB cases and 250 unlikely PTB cases will be collected. An AI-CXR algorithm (qXR) will be used to process CXRs. The primary endpoint will be sensitivity and specificity of AI to detect confirmed and unconfirmed PTB cases (composite reference standard); a secondary endpoint will be evaluated for confirmed PTB cases (microbiological reference standard). In stage II, a multi-reader multi-case study using a cross-over design will be conducted with 16 readers and 350 CXRs to assess the usefulness of AI-assisted CXR interpretation for readers (clinicians and radiologists). The primary endpoint will be the difference in the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of readers with and without AI assistance in correctly classifying CXRs as per RRS.
Ethics and dissemination: The study has been approved by a local institutional ethics committee at each site. Results will be published in academic journals and presented at conferences. Data will be made available as an open-source database.
Study registration number: PACTR202502517486411.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence; Chest imaging; Diagnostic radiology; Paediatric infectious disease & immunisation; Pulmonary Disease; Tuberculosis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: DR and JAC are employees of Qure.ai. Other authors declare that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Global tuberculosis report. 2024 https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tb-reports/globa... Available.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
