Therapeutic Potential of Lactobacillus rhamnosus DS3316 via Cell Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 40730488
- PMCID: PMC12324992
- DOI: 10.4014/jmb.2505.05001
Therapeutic Potential of Lactobacillus rhamnosus DS3316 via Cell Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
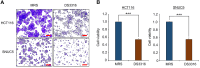
Colorectal cancer (CRC) has a very high mortality rate worldwide. Although various therapies have been developed to treat CRC, the need for novel therapeutic approaches has been increasing due to severe side effects and limited efficacy of current treatments. Recently, although research on the gut microbiome and its association with colon cancer has been growing, the mechanisms of gut microbiome inhibition in CRC remain insufficiently understood. Thus, in this study, we investigated the growth-inhibitory effects of the culture supernatant of Lactobacillus rhamnosus DS3316, isolated from infant feces, on CRC cell lines (HCT116 and SNUC5). And RNA-seq analysis revealed an increase in apoptosis-related terms induced by L. rhamnosus DS3316 treatment. Also, we found the non-toxicity of L. rhamnosus DS3316 in human iPSC-derived intenstine organoid. Thus, we suggested that L. rhamnosus DS3316 inhibits the growth of colorectal cancer cell lines without affecting normal cells. And L. rhamnosus DS3316 is expected to be a promising candidate for the development of microbiome-based colorectal cancer therapies. Furthermore, its combined use with various colorectal cancer treatment methods could lead to the proposal of more effective therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: Lactobacillus rhamnosus; apoptosis; colorectal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The potential probiotic role of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus on growth performance, gut health, and immune responses of weaned pigs.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf089. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf089. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 40125886
-
3-O-Acetyl-11-Keto-β-Boswellic Acid Suppresses Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer by Inhibiting the NF-Kb Signaling Pathway and Remodeling Gut Microbiota.Oncol Res. 2025 Jul 18;33(8):1969-1989. doi: 10.32604/or.2025.062386. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40746878 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis-Inducing Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum DS0709 in Colorectal Cancer.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Aug 15;35:e2504042. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2504.04042. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40825676
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
References
-
- Duan B, Zhao Y, Bai J, Wang J, Duan X, Luo X, et al. 2022. Colorectal Cancer: An Overview, In Morgado-Diaz JA (ed.), Gastrointestinal Cancers, Ed., Brisbane (AU).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

