Derivation of resident macrophages and construction of tumor microenvironment in Flk-1-knockout chimeric mice produced via blastocyst complementation
- PMID: 40730607
- PMCID: PMC12307763
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-12571-w
Derivation of resident macrophages and construction of tumor microenvironment in Flk-1-knockout chimeric mice produced via blastocyst complementation
Abstract
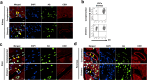
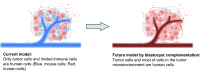
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is deeply involved in cancer progression and treatment resistance. Although humanized mouse models have been developed by transplanting human cells into immunodeficient mice, they fail to fully reconstitute the TME. Blastocyst complementation using Flk-1 (Vegfr2, Kdr) knockout hosts offers a potential solution. However, the generation of interspecies human-mouse chimeras using blastocyst complementation has not yet been successful. As a foundational step, this study aims to demonstrate that donor-derived TME can be constructed using this method in intraspecies chimeric mice. We generated chimeric mice by injecting Azami-Green (AG)-positive C57BL/6 (B6) mouse-derived embryonic stem cells (ESCs) into ICR Flk-1 knockout embryos. We observed that vascular endothelial cells (VECs), hematopoietic cells, and tissue-resident macrophages were derived from the injected AG-positive ESCs. We engrafted B6-derived tumor cells into the chimeras and identified tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, tumor-associated macrophages, and VECs derived from donor cells. Moreover, tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells in these chimeric mice showed cytotoxic activity comparable to that in wild-type mice. We anticipate that this intraspecies chimeric mouse model can serve as a valuable tool for basic research. Furthermore, future humanized tumor models generated via blastocyst complementation have the potential to significantly advance anticancer drug development in the preclinical phase.
Keywords: Blastocyst complementation; Resident macrophages; Tumor microenvironment; Tumor model.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Generation of Pulmonary Endothelial Progenitor Cells for Cell-based Therapy Using Interspecies Mouse-Rat Chimeras.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021 Aug 1;204(3):326-338. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202003-0758OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33705684 Free PMC article.
-
Maturation Status of Rat Lung Epithelial Cells in Interspecies Chimeras Generated by Blastocyst Complementation.Genes Cells. 2025 Sep;30(5):e70046. doi: 10.1111/gtc.70046. Genes Cells. 2025. PMID: 40840556
-
Tumor therapy by targeting extracellular hydroxyapatite using novel drugs: A paradigm shift.Cancer Med. 2024 Feb;13(3):e6812. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6812. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38239047 Free PMC article.
-
Fabricating mice and dementia: opening up relations in multi-species research.In: Jenkins N, Jack-Waugh A, Ritchie L, editors. Multi-Species Dementia Studies. Bristol (UK): Bristol University Press; 2025 Feb 25. Chapter 2. In: Jenkins N, Jack-Waugh A, Ritchie L, editors. Multi-Species Dementia Studies. Bristol (UK): Bristol University Press; 2025 Feb 25. Chapter 2. PMID: 40690569 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wege, A. K. Humanized mouse models for the preclinical assessment of cancer immunotherapy. BioDrugs32, 245–266 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

