Circulating microRNA profiles in early-stage osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 40730797
- PMCID: PMC12307603
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-07922-6
Circulating microRNA profiles in early-stage osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
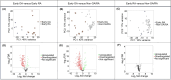
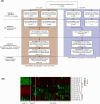
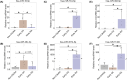
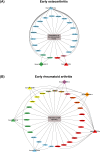
Osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are prevalent joint diseases, yet early diagnosis remains challenging with existing methods. Circulating microRNAs are promising biomarkers for detection and differentiation of arthritis subtypes. This study aimed to profile plasma microRNAs from early OA (N = 22), early RA (N = 12), and non-OA/RA (N = 50) individuals using microRNA-sequencing. Principal component analysis revealed distinct clustering of early OA from both early RA and non-OA/RA, but not for early RA and non-OA/RA. A total of 170 differentially expressed microRNAs were identified in early OA versus the other groups, with no significant differences found between early RA and non-OA/RA. Stepwise filtering followed by RT-qPCR validation in independent samples identified six microRNAs: miR-16-5p and miR-29c-3p were upregulated in early OA compared to both early RA and non-OA/RA, while miR-744-5p, miR-382-5p, miR-3074-5p, and miR-11400 were upregulated in early RA compared to the other two groups. Additionally, three novel microRNAs were identified using bioinformatic tools-one enriched in early OA and two in early RA. Target prediction and pathway analyses revealed that early OA microRNAs were linked to extracellular matrix degradation pathways, and early RA microRNAs were linked to immune signaling. These findings highlight six known and three novel circulating microRNAs with potential as biomarkers to distinguish early OA from early RA.
Keywords: Biomarker; Epigenetics; Human; Novel microRNAs; Plasma; microRNA-sequencing.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: S.A.A. declares that she has filed a US Provisional Patent Application no. 63/033,463 titled Circulating MicroRNAs in Knee Osteoarthritis and Uses Thereof. All other authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All participants provided written informed consent to be included in this study. The study protocol followed guidelines set by the Henry Ford Health Institutional Review Board (IRB #13995). Additional ethics approval was provided by the VA Tennessee Healthcare System (IRB #1643056 and IRB #1722175), and the OAI via University of California, San Francisco (FWA approval # 00000068; IRB approval # 10-00532).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Shared molecular biomarkers and therapeutic targets in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis: Focus on EIF3B, KHSRP, NCL, PDCD1LG2, and SLC25A37.Cytokine. 2025 Sep;193:156988. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2025.156988. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Cytokine. 2025. PMID: 40592131
-
Circulating miR-28-5p is overexpressed in patients with sarcopenia despite long-term remission of Cushing's syndrome: a pilot study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 17;15:1410080. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1410080. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39086897 Free PMC article.
-
A 14-Day Plant-Based Dietary Intervention Modulates the Plasma Levels of Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated MicroRNAs: A Bioinformatics-Guided Pilot Study.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 4;17(13):2222. doi: 10.3390/nu17132222. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40647325 Free PMC article.
-
Mobile bearing vs fixed bearing prostheses for posterior cruciate retaining total knee arthroplasty for postoperative functional status in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Feb 4;2015(2):CD003130. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003130.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25650566 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclooxygenase-2 selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (etodolac, meloxicam, celecoxib, rofecoxib, etoricoxib, valdecoxib and lumiracoxib) for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Apr;12(11):1-278, iii. doi: 10.3310/hta12110. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18405470
References
-
- Kurdi, A. J., Voss, B. A., Tzeng, T. H., Scaife, S. L., El-Othmani, M. M. & Saleh, K. J. Rheumatoid arthritis vs osteoarthritis: Comparison of demographics and trends of joint replacement data from the nationwide inpatient sample. Am. J. Orthop. (Belle Mead NJ).47 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

