Building a dynamic web calculator for individualized conditional survival estimation in brainstem ependymoma
- PMID: 40730852
- PMCID: PMC12307898
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-12428-2
Building a dynamic web calculator for individualized conditional survival estimation in brainstem ependymoma
Abstract
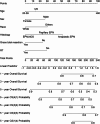
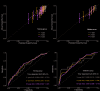
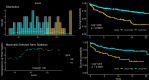
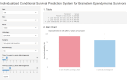
Brainstem ependymomas (EPNs) are rare and aggressive central nervous system tumors with unique anatomical challenges and poor prognosis. Traditional survival estimates offer limited clinical guidance due to their static nature. This study aimed to investigate the dynamic survival patterns of brainstem EPNs using conditional survival (CS) analysis and to develop a web-based nomogram model for individualized, real-time prognostication. Patients diagnosed with primary brainstem EPNs between 2000 and 2021 were identified from the SEER database. CS analysis was performed to assess changes in survival probability over time. Annual hazard rates were calculated to identify high-risk periods. Prognostic variables were selected using best subset regression (BSR) and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) methods. A CS-based nomogram was constructed using multivariable Cox regression and validated through calibration plots, ROC curves, and decision curve analysis (DCA). A risk stratification system and an interactive web calculator were also developed. A total of 697 patients were included and randomly assigned to training (n = 487) and validation (n = 210) cohorts. CS analysis showed that as patients survive longer after diagnosis, their probability of surviving additional years increases steadily. And six variables (age, sex, race, histology, surgery, and radiotherapy) were identified via the LASSO model for nomogram construction. The CS-nomogram demonstrated good calibration and acceptable discrimination, with 1-, 3-, and 5-year AUCs of 0.626, 0.649, and 0.656 in the training cohort, and 0.688, 0.692, and 0.687 in the validation cohort, respectively. DCA confirmed the clinical utility of the model. A risk classification system effectively stratified patients into high- and low-risk groups with significantly different survival outcomes. A web-based calculator was created to facilitate real-world application. This study presents a novel CS-based nomogram that dynamically predicts survival in patients with brainstem EPNs. By capturing time-dependent survival probabilities and integrating key clinical factors, the model offers a practical tool to support individualized prognosis, patient counseling, and follow-up planning in clinical practice. While it offers individualized prognostic insights, its clinical use requires further external validation.
Keywords: Brainstem ependymomas; Conditional survival; Nomogram; Prognosis prediction; SEER.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Conflict of interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Clinical diagnostic and prognostic value of homocysteine combined with hemoglobin [f (Hcy-Hb)] in cardio-renal syndrome caused by primary acute myocardial infarction.J Transl Med. 2025 Jul 23;23(1):813. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06512-4. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40702542 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
A prognostic nomogram and risk classification system of elderly patients with extraosseous plasmacytoma: a SEER database analysis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Dec;149(20):17921-17931. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05492-6. Epub 2023 Nov 13. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37955685 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840
References
-
- Michele, R., Gemma, G., Elena, M. & Charles, V. J. C. R. O. H. Ependymoma. 63. (2007).
-
- Amr, H. S., Nardin, S., Kyle, J. & Mohammad, H. S. Michael D T, Michael G FJNRC: the biology of ependymomas and emerging novel therapies. 22. (2022).
-
- Courtney, S. M., Kristin, L. S. & Paul, G. F. J. J. N. Incidence patterns for ependymoma: a surveillance, epidemiology, and end results study. 110. (2008). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

