Comprehensive identification, stress responses and protein-protein interactions of the ferredoxin gene family in the fast-growing tree species Paulownia fortunei
- PMID: 40730946
- PMCID: PMC12306049
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-025-06909-9
Comprehensive identification, stress responses and protein-protein interactions of the ferredoxin gene family in the fast-growing tree species Paulownia fortunei
Abstract
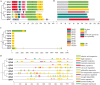
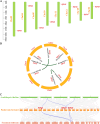
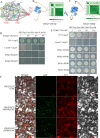
Paulownia fortunei is a significant fast-growing economic tree species with wide industrial value, and studies have revealed that its rapid growth mechanism is associated with its C3-CAM photosynthetic characteristics. Ferredoxin, a key protein in the plant photosynthetic electron transport chain, plays a crucial role in both C3 and CAM pathways. In addition to participating in plant photosynthesis and carbon assimilation, ferredoxin also plays important roles in plant nitrogen assimilation, sulfur metabolism, and responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. In this study, bioinformatics analysis was utilized to identify eight members of the ferredoxin gene family in Paulownia fortunei, categorized into four subfamilies distributed across eight different chromosomes. All members contain a 2Fe-2 S domain and light-responsive elements, displaying high conservation among subfamily members. Transcriptome analysis and real-time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) assays indicated that photosynthetic ferredoxins PfFd1 and PfFd2 play important roles in the response of Paulownia fortunei to droughts, salt and pathogen stresses. Yeast two-hybrid(Y2H)results showed that PfFd1 and PfFd2 can form heterodimers. Interaction predictions, Y2H, and bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) experiments verified direct interactions between the major photosynthetic ferredoxin PfFd2 and ferredoxin-NADP + reductase (FNR) as well as sulfite reductase (SIR) in Paulownia fortunei, suggesting that PfFd2 may play a significant role in photosynthetic electron transport and sulfur metabolism in Paulownia fortunei, implying its potential association with the fast-growing characteristics of Paulownia fortunei and its influence on normal growth and metabolism. Additionally, the interaction between the Paulownia witches' broom phytoplasma effector pawb3 and PfFd2 was verified through Y2H and GST pull-down experiments, suggesting that PfFd2 may be related to disease resistance in Paulownia fortunei. This study systematically analyzed the family characteristics of ferredoxins in Paulownia fortunei and preliminary explored their biological functions, providing a theoretical basis for future in-depth exploration of molecular mechanisms related to plant fast growth and the cultivation of high-resistance, fast-growing germplasm resources.
Keywords: Paulownia fortunei; Fast-growing; Ferredoxin; Stress response.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable in this study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Identification of PLATZ gene family in Camellia sinensis and expression analysis of this gene family under high temperature and drought stresses].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2025 Jul 25;41(7):2897-2912. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.240969. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40769568 Chinese.
-
[Identification of the sugarcane β-1,3-glucanase gene family and analysis of their expression under various stress conditions].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2025 Jul 25;41(7):2913-2933. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.250001. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40769569 Chinese.
-
Genome-wide identification of peanut ERFs and functional characterization of AhERF28 in response to salt and drought stresses.Plant Cell Rep. 2025 Jul 1;44(7):165. doi: 10.1007/s00299-025-03557-z. Plant Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 40593149
-
Paulownia Witches' Broom Disease: A Comprehensive Review.Microorganisms. 2024 Apr 28;12(5):885. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12050885. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38792713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
References
-
- Churkina G, Schimel D, Braswell BH, et al. Spatial analysis of growing season length control over net ecosystem exchange. Glob Change Biol. 2005;11(10):1777–87.
-
- Drake JE, Power SA, Duursma RA, et al. Stomatal and non-stomatal limitations of photosynthesis for four tree species under drought: a comparison of model formulations. Agric Forest Meteorol. 2017;247:454–66.
-
- Reich PB, Sendall KM, Stefanski A, et al. Effects of climate warming on photosynthesis in boreal tree species depend on soil moisture. Nature. 2018;562(7726):263. - PubMed
-
- Milliken AL, Fan M, Mathan J, et al. Measuring nonfoliar photosynthesis. Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2790:77–94. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 252102110337/Henan Provincial Science and Technology Research Project
- Grant No. 2016YFD0600106/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 224400510018/Germplasm Innovation, Development and Application of Characteristic Economic Plants
- 224200510010/Project of Central Plains Science and Technology Innovation Leading Talents of Henan Province
- 30601986/Special project for the construction of central plains scholars and scientists' studios
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

