A scoping review of artificial intelligence applications in clinical trial risk assessment
- PMID: 40731070
- PMCID: PMC12307910
- DOI: 10.1038/s41746-025-01886-7
A scoping review of artificial intelligence applications in clinical trial risk assessment
Abstract
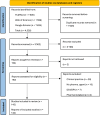
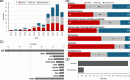
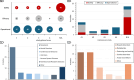
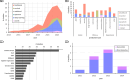
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly applied to clinical trial risk assessment, aiming to improve safety and efficiency. This scoping review analyzed 142 studies published between 2013 and 2024, focusing on safety (n = 55), efficacy (n = 46), and operational (n = 45) risk prediction. AI techniques, including traditional machine learning, deep learning (e.g., graph neural networks, transformers), and causal machine learning, are used for tasks like adverse drug event prediction, treatment effect estimation, and phase transition prediction. These methods utilize diverse data sources, from molecular structures and clinical trial protocols to patient data and scientific publications. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have seen a surge in applications, featuring in 7 out of 33 studies in 2023. While some models achieve high performance (AUROC up to 96%), challenges remain, including selection bias, limited prospective studies, and data quality issues. Despite these limitations, AI-based risk assessment holds substantial promise for transforming clinical trials, particularly through improved risk-based monitoring frameworks.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- DiMasi, J. A., Feldman, L., Seckler, A. & Wilson, A. Trends in risks associated with new drug development: success rates for investigational drugs. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther.87, 272–277 (2010). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

