An Evaluation of Turkish Dentists' Approach to Indirect Pulp Capping and Material Preferences: A Questionnaire-Based Survey
- PMID: 40731750
- PMCID: PMC12298376
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina61071120
An Evaluation of Turkish Dentists' Approach to Indirect Pulp Capping and Material Preferences: A Questionnaire-Based Survey
Abstract
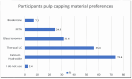
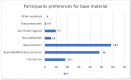
Background and Objectives: The aim of this study was to evaluate how the indirect pulp capping treatment approaches and material choices used by dentists actively practicing in Turkey vary according to demographic data. Materials and Methods: Dentists practicing in Turkey were included in this study. A 13-question survey was used and distributed to the participants via social media. The statistical analysis of the data obtained from this study was performed using IBM SPSS v23. The chi-square test was used to compare categorical variables between groups, and multiple comparisons of the proportions were analyzed using the Bonferroni correction. The results of the analysis are presented as frequencies (percentages) for categorical data. The significance level was set at p < 0.05. Results: A total of 402 dentists from across Turkey participated in this study. A total of 331 participants (82.3%) reported that they performed indirect pulp capping treatment. The most commonly used materials for indirect pulp capping were Ca(OH)2;-containing liners (73.4%) and glass ionomer cement (58.3%). The use of amalgam and cotton roll isolation was more common among dentists working in the public sector, whereas rubber dam isolation and the use of contemporary materials such as MTA and Biodentine were more frequently observed among dentists working in the private sector. Conclusions: Significant differences were found in the dentists' indirect pulp capping approaches and the materials they used based on their specialty, years of experience, and workplace setting. These findings suggest that dentists' knowledge and experience regarding indirect pulp capping should be enhanced during their education and post-graduation training.
Keywords: dental pulp capping; dentistry; surveys and questionnaires.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources