Conservative Treatment of Sesamoiditis: A Systematic Literature Review with Individual-Level Pooled Data Analysis
- PMID: 40731844
- PMCID: PMC12300395
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina61071215
Conservative Treatment of Sesamoiditis: A Systematic Literature Review with Individual-Level Pooled Data Analysis
Abstract
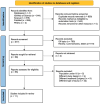
Background and Objectives: Sesamoiditis is a painful and functionally limiting condition that affects the sesamoid bones of the hallux, frequently seen in athletic populations. Despite its clinical relevance, there are no standardised guidelines for its conservative management. This systematic review aims to evaluate the effectiveness of conservative treatments for sesamoiditis by summarising individual-level data from published studies. Materials and Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted in PubMed/MEDLINE, Scopus, ISI/Web of Science, and PEDro (Physiotherapy Evidence Database) up to December 2024 in accordance with PRISMA 2020 guidelines and following a protocol specifically devised for rare or underrepresented medical conditions. Eligible studies included case reports and case series involving patients aged ≥16 years who were conservatively treated for clinically and/or radiologically diagnosed sesamoiditis. Data on patient demographics, diagnosis, type and duration of treatment, pain- (Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and Numeric Rating Scale (NRS)) and function-related (Foot and Ankle Ability Measure (FAAM) and Foot and Ankle Outcome Score (FAOS)) outcomes, and return to activity were extracted. Study quality was assessed using Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) critical appraisal tools. Pooled effect sizes were computed where applicable. Results: Out of 2380 initial records, 11 studies comprising 59 patients (29 females) were included. Treatments varied widely, including orthotics, corticosteroid injections, physical therapy, and biologic approaches such as concentrated bone marrow aspirate (CBMA). VAS scores improved in 66% of cases. NRS scores returned to baseline in some patients after initial improvement, revealing recurrence. FAAM and FAOS subscales showed functional improvements, particularly in sports-specific domains. Return to activity varied: in a case series, 45.4% resumed pain-free sports participation, while others remained symptomatic. Conclusions: Conservative treatment options for sesamoiditis showed variable effectiveness with promising outcomes in selected patients. Corticosteroid injections and orthotics appeared beneficial, but high recurrence and limited functional recovery persisted in some cases. Standardised treatment protocols and high-quality prospective studies are needed to improve clinical decision-making and optimise non-surgical management.
Keywords: conservative treatment; return to sport; sesamoiditis; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources