Probiotic Supplementation Improves Gut Microbiota in Chronic Metabolic and Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases Among Chinese Adults over 60: Study Using Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Cohorts
- PMID: 40732015
- PMCID: PMC12299297
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13071507
Probiotic Supplementation Improves Gut Microbiota in Chronic Metabolic and Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases Among Chinese Adults over 60: Study Using Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Cohorts
Abstract
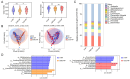
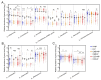
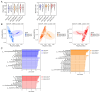
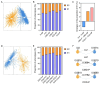
Probiotics demonstrate the ability to maintain intestinal homeostasis and promote gut health. However, their effects on gut microbiota in adults over 60 years old with chronic metabolic disease (CMD) or cardio-cerebrovascular disease (CCD) remain poorly understood. This study analyzed 1586 stool samples from 1377 adults (CMD, CCD, and healthy controls) using 16S rRNA sequencing. Cohort 1 (n = 1168) was used for cross-sectional analysis, while cohort 2 (n = 209) underwent longitudinal assessment over approximately 13 months. The results demonstrated that probiotics promoted significant gut microbiota alterations across both cohorts. Probiotic supplementation significantly increased lactobacilli in the CMD, CCD, and H groups. In both cohorts, probiotic supplementation enhanced Butyricicoccus, Clostridium sensu stricto 1, and Coprococcus in H groups, enhanced Anaerostipes and Fusicatenibacter in CMD groups, and reduced Haemophilus and Lachnospira in CCD groups. Notably, long-term supplementation not only elevated Dorea, Eubacterium hallii group, and Blautia in all groups but also suppressed Klebsiella and Bilophila in the CMD and CCD groups. Enterotype analysis revealed that probiotics increased the proportion of enterotype 1 and transition probabilities from enterotype 2 to 1 in the CMD and CCD groups, demonstrating that CCD/CMD gut microbiota exhibited greater responsiveness to probiotic modulation. Overall, this study suggests probiotics' role in modulating adult gut microbiota and their potential benefits in chronic metabolic and cardio-cerebrovascular diseases.
Keywords: 16S rRNA gene sequencing; cross-sectional cohort; gut microbiota; longitudinal cohort; probiotic supplementation.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Yan Liu was employed by the company Yingdong Intelligent Technology (Shandong) Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of supplementation of live and heat-treated Bifidobacterium animalis subspecies lactis CECT 8145 on glycemic and insulinemic response, fecal microbiota, systemic biomarkers of inflammation, and white blood cell gene expression of adult dogs.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae291. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae291. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39320367
-
Probiotics for the prevention of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea in adults and children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 19;12(12):CD006095. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006095.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29257353 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Probiotics Supplementation on REM Sleep Behavior Disorder and Motor Symptoms in Parkinson's Disease: A Pilot Study.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Jul;31(7):e70541. doi: 10.1111/cns.70541. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40717466 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Probiotics for the prevention of pediatric antibiotic-associated diarrhea.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Dec 22;(12):CD004827. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004827.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Apr 30;4:CD004827. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004827.pub5. PMID: 26695080 Updated.
-
Probiotics for the prevention of pediatric antibiotic-associated diarrhea.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Nov 9;(11):CD004827. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004827.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Dec 22;(12):CD004827. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004827.pub4. PMID: 22071814 Updated.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

