Paenibacillus hubeiensis sp. nov.: A Novel Selenium-Resistant Bacterium Isolated from the Rhizosphere of Galinsoga parviflora in a Selenium-Rich Region of Enshi, Hubei Province
- PMID: 40732068
- PMCID: PMC12300063
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13071559
Paenibacillus hubeiensis sp. nov.: A Novel Selenium-Resistant Bacterium Isolated from the Rhizosphere of Galinsoga parviflora in a Selenium-Rich Region of Enshi, Hubei Province
Abstract
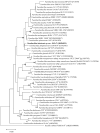
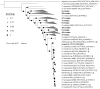
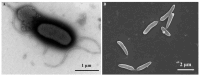
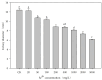
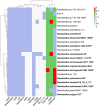
ES5-4T, a Gram-positive, motile, aerobic, and rod-shaped strain, was isolated from the rhizosphere of Galinsoga parviflora growing in the selenium-rich ore area of Enshi, Hubei Province, China. This strain can grow at pH levels of 5.0-10.0 and temperatures of 4-42 °C, with optimal growth at pH 7.0 and 28 °C. It was found to resist NaCl up to 5% (w/v), with an optimal growth condition of 0.5-1.0%. The strain exhibited tolerance to selenite (Se4+) concentrations up to 5000 mg/L. The major fatty acids of the ES5-4T strain were anteiso-C15:0 (46.5%) and C16:0 (21.7%), its predominant respiratory quinone was MK-7, and its polar lipids included diphosphatidylglycerol (DPG), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylglycerol (PG), and an unidentified phospholipid (PL). The presence of the 16S rRNA gene sequence implies that ES5-4T belongs to a member of the genus Paenibacillus, with the highest sequence similarity of 98.4% to Paenibacillus pabuli NBRC 13638T. The bac120 tree also confirmed that the strain is within the genus Paenibacillus. The average nucleotide identity (ANI) and digital DNA-DNA hybridization (dDDH) values between ES5-4T and closely related members of the genus Paenibacillus were all below the cutoff levels of 95-96% and 70%, respectively. Based on a polyphasic approach, including phenotypic, chemotaxonomic, and phylogenetic analyses, the ES5-4T strain is proposed as a novel species of the genus Paenibacillus, for which the name Paenibacillus hubeiensis sp. nov. is proposed. This type strain is designated as ES5-4T (=GDMCC 1.3540T = KCTC 43478T).
Keywords: Paenibacillus hubeiensis sp. nov.; bac120 tree; polyphasic analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phylotaxonomic analysis uncovers underestimated species diversity within the genus Rossellomorea with description of selenium-resistant Rossellomorea yichunensis sp. nov.BMC Microbiol. 2025 Jul 3;25(1):408. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-04138-6. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40610858 Free PMC article.
-
Description of Paenibacillus jiagnxiensis sp. nov., a mesotrione-degrading bacterium isolated from farmland and cloning of a novel mesotrione nitroreductase gene.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2025 Jun 29;118(8):98. doi: 10.1007/s10482-025-02114-8. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2025. PMID: 40581877
-
Genomic and taxonomic characterization of Niallia pakistanensis sp. nov. NCCP-28T: a novel antibiotic-resistant and heavy-metal-tolerant bacterium isolated from the legume rhizosphere in Pakistan.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2025 Jul 23;118(9):122. doi: 10.1007/s10482-025-02132-6. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2025. PMID: 40702293
-
Lentibacillus songyuanensis sp. nov., A Drought- and Salt- Tolerant Bacterium with Ability to Degrade Aniline Blue Isolated from Saline-Alkali Soil.Curr Microbiol. 2025 Aug 25;82(10):475. doi: 10.1007/s00284-025-04445-1. Curr Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40853388
-
Desulfosporosinus sediminicola sp. nov., an acidophilic sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated from acidic sediments of a disused iron mine site.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2025 Aug 28;118(10):142. doi: 10.1007/s10482-025-02152-2. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2025. PMID: 40875059
References
-
- Shida O., Takagi H., Kadowaki K., Nakamura L.K., Komagata K. Transfer of Bacillus alginolyticus, Bacillus chondroitinus, Bacillus curdlanolyticus, Bacillus glucanolyticus, Bacillus kobensis, and Bacillus thiaminolyticus to the genus Paenibacillus and emended description of the genus Paenibacillus. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1997;47:289–298. doi: 10.1099/00207713-47-2-289. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

