Harnessing Waste Bread: From Potential Use in Microbial Growth and Enzyme Production to Techno-Economic Assessment
- PMID: 40732080
- PMCID: PMC12300665
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13071571
Harnessing Waste Bread: From Potential Use in Microbial Growth and Enzyme Production to Techno-Economic Assessment
Abstract
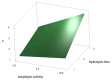
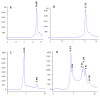
This study highlights waste bread (WB) as a novel, cost-effective, and nutrient-rich substrate for microbial growth, offering a sustainable alternative to conventional media. As a renewable resource, WB promotes the circular economy by reducing food waste and encouraging biotechnological innovation. The incorporation of WB into microbial culture media enhanced the growth of various reference strains (E. coli, E. faecalis, P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus), with at least a two-fold increase compared to conventional Luria-Bertani (LB) medium. Moreover, combining 2% WB with diluted LB (1/10) reduced medium costs by up to 90%. Furthermore, it was confirmed that 1% WB can effectively replace starch during the screening of amylolytic strains. Applying a fractional factorial design, the production of amylase by Bacillus sp. BSS (Amy-BSS) was enhanced 15-fold. An analysis of the Pareto diagram revealed that WB was the most significant factor. Additionally, Amy-BSS was applied to hydrolyze polysaccharides in WB, enabling the generation of high-value-added products in food processing. This hydrolysis process yielded 4.6 g/L of fermentable sugars from 1% WB. Evaluating the economic feasibility of WB valorization into value-added products elucidates potential pathways for cost reduction and enhanced environmental sustainability, thereby positioning WB as a viable tool for sustainable development.
Keywords: Bacillus; amylase; microorganisms; techno-economic assessment; waste bread.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Wood Waste Valorization and Classification Approaches: A systematic review.Open Res Eur. 2025 May 6;5:5. doi: 10.12688/openreseurope.18862.2. eCollection 2025. Open Res Eur. 2025. PMID: 40438563 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
The INTRABEAM® Photon Radiotherapy System for the adjuvant treatment of early breast cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2015 Aug;19(69):1-190. doi: 10.3310/hta19690. Health Technol Assess. 2015. PMID: 26323045 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
References
-
- Tamasiga P., Ouassou E.H., Onyeaka H., Bakwena M., Happonen A., Molala M. Forecasting disruptions in global food value chains to tackle food insecurity: The role of AI and big data analytics—A bibliometric and scientometric analysis. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023;14:100819. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2023.100819. - DOI
-
- Hafyan R.H., Mohanarajan J., Uppal M., Kumar V., Narisetty V., Maity S.K., Gadkari S. Waste bread valorization: A review of sustainability aspects and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2024;8:1334801. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1334801. - DOI
-
- Aït-Kaddour A., Hassoun A., Tarchi I., Loudiyi M., Boukria O., Cahyana Y., Ozogul F., Khwaldia K. Transforming plant-based waste and by-products into valuable products using various “Food Industry 4.0” enabling technologies: A literature review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024;955:176872. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.176872. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

