Multiparametric Evaluation of Tetradesmus obliquus Biomass: An Integrated Approach Including Antioxidant, Nutritional, and Energy Properties
- PMID: 40732092
- PMCID: PMC12299801
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13071583
Multiparametric Evaluation of Tetradesmus obliquus Biomass: An Integrated Approach Including Antioxidant, Nutritional, and Energy Properties
Abstract
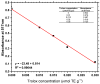
The microalga Tetradesmus obliquus has emerged as a promising candidate for biotechnological and industrial applications due to its rapid growth, resilience under diverse environmental conditions, and potential for bioactive compound production. This study presents a multiparametric characterization of dry T. obliquus biomass cultivated in patented industrial-scale photobioreactors, integrating thermochemical, elemental, antioxidant, and protein analyses. Proximate and ultimate analyses were conducted to assess fuel potential, revealing favorable volatile matter (VM = 64.80-72.44%) and fixed carbon (FC = 15.77-21.23%) contents. The HHV (18.32-22.75 MJ·kg-1) and LHV (16.86-21.24 MJ·kg-1) confirmed the biomass as a viable candidate for solid biofuel. The elemental composition provided the total nitrogen values, subsequently used to estimate the protein content via both the Kjeldahl and Dumas methods, with results ranging from 36.66% to 40.02%, in line with the literature. Despite the absence of detectable antioxidant activity under the tested DPPH conditions, the biomass demonstrated a robust nutritional profile and energy potential. These findings support the industrial relevance of T. obliquus biomass, particularly for applications targeting sustainable protein sources and bioenergy solutions.
Keywords: antioxidant; bioproducts; calorific value; industrial photobioreactors; microalgal biomass; physicochemical composition; protein content.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Production of Bioproducts from Wastewater Treatment Using the Microalga Neochloris oleoabundans.Eng Life Sci. 2025 Jul 3;25(7):e70032. doi: 10.1002/elsc.70032. eCollection 2025 Jul. Eng Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40621450 Free PMC article.
-
Combustion reactivity of hydrothermally derived biochar from sugarcane green harvesting residues (GHR): An evaluation as a solid fuel.Bioresour Technol. 2025 Oct;434:132843. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2025.132843. Epub 2025 Jun 17. Bioresour Technol. 2025. PMID: 40554016
-
Torrefaction of Sericulture Agro-Industrial Waste for Sustainable Waste-to-Resource Solutions.ACS Omega. 2025 Jun 13;10(25):27223-27237. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c02508. eCollection 2025 Jul 1. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40630725 Free PMC article.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Enteral nutritional therapy for induction of remission in Crohn's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD000542. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000542.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Apr 01;4:CD000542. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000542.pub3. PMID: 17253452 Updated.
References
-
- Razzak S.A., Bahar K., Oajedul Islam K.M., Haniffa A.K., Faruque M.O., Zakir Hossain S.M., Hossain M.M. Microalgae cultivation in photobioreactors: Sustainable solutions for a greener future. Green Chem. Eng. 2024;5:418–439. doi: 10.1016/j.gce.2023.10.004. - DOI
-
- Rörig L.R., Gressler P.D., Tramontin D.P., Schneider R.C.S., Derner R.B., Bastos E.O., Souza M.P., Oliveira C.Y.B. Biomass productivity and characterization of Tetradesmus obliquus grown in a hybrid photobioreactor. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2024;47:367–380. doi: 10.1007/s00449-024-02969-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Penloglou G., Pavlou A., Kiparissides C. Recent Advancements in Photo-Bioreactors for Microalgae Cultivation: A Brief Overview. Processes. 2024;12:1104. doi: 10.3390/pr12061104. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

