The Characterization of a Gonococcal HicAB Toxin-Antitoxin System Capable of Causing Bacteriostatic Growth Arrest
- PMID: 40732128
- PMCID: PMC12297915
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13071619
The Characterization of a Gonococcal HicAB Toxin-Antitoxin System Capable of Causing Bacteriostatic Growth Arrest
Abstract
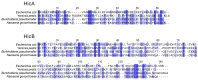
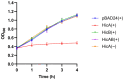
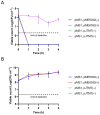
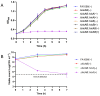
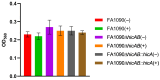
Neisseria gonorrhoeae is the causative agent of the sexually transmitted infection gonorrhea. Preventative vaccines or novel treatments based on a better understanding of the molecular basis of N. gonorrhoeae infection are required as resistance to current antibiotics is widespread. Toxin-antitoxin (TA) systems modulate bacterial physiology by interfering with vital cellular processes; type II TA systems, where both toxin and antitoxin are proteins, are the best-studied. Bioinformatics analysis revealed genes encoding an uncharacterized type II HicAB TA system in the N. gonorrhoeae strain FA1090 chromosome, which were also present in >83% of the other gonococcal genome sequences examined. Gonococcal HicA overproduction inhibited bacterial growth in Escherichia coli, an effect that could be counteracted by the co-expression of HicB. Kill/rescue assays showed that this effect was bacteriostatic rather than bactericidal. The site-directed mutagenesis of key histidine and glycine residues (Gly22, His24, His29) abolished HicA-mediated growth arrest. N. gonorrhoeae FA1090∆hicAB and complemented derivatives that expressed IPTG-inducible hicA, hicB, or hicAB, respectively, grew as wild type, except for IPTG-induced FA1090∆hicAB::hicA. RT-PCR demonstrated that hicAB are transcribed in vitro under the culture conditions used. The deletion of hicAB had no effect on biofilm formation. Our study describes the first characterization of a HicAB TA system in N. gonorrhoeae.
Keywords: HicA; HicAB; HicB; Neisseria gonorrhoeae; bacteriophage; biofilm; growth arrest; toxin–antitoxin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gentamicin induction of the gonococcal hicAB toxin-antitoxin-encoding system and impact on gene expression influencing biofilm formation and in vivo fitness in a strain-specific manner.mBio. 2025 Jul 30:e0159525. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01595-25. Online ahead of print. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40736253
-
Gentamicin induction of the gonococcal hicAB toxin-antitoxin encoding system and impact on gene expression influencing biofilm formation and in vivo fitness in a strain-specific manner.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 11:2025.06.11.659166. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.11.659166. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: mBio. 2025 Jul 30:e0159525. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01595-25. PMID: 40568169 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The gonococcal vaccine candidate antigen NGO1701 is a N. gonorrhoeae periplasmic copper storage protein.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 7:2025.05.01.651437. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.01.651437. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40654730 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Antibiotics for treating gonorrhoea in pregnancy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 21;2(2):CD011167. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011167.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29465747 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

