Novel Treatments for Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 40732148
- PMCID: PMC12300781
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13071639
Novel Treatments for Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis: A Narrative Review
Abstract
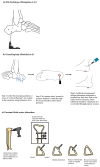
Diabetic foot osteomyelitis (DFO) is a severe complication of diabetes mellitus and a leading cause of non-traumatic lower extremity amputation. Treatment remains clinically challenging with high recurrence rates despite standard antibiotic therapy and surgical debridement. This narrative review synthesizes current evidence on novel operative and nonoperative therapies for DFO, focusing on emerging biomaterials, local antibiotic delivery systems, innovative surgical techniques, and adjunctive topical agents. Studies examining bioabsorbable and nonabsorbable antibiotic carriers, such as calcium sulfate beads, collagen sponges, and bioactive glass, demonstrate promising infection resolution rates and a potential to reduce the surgical burden, though most are limited by small cohorts and observational designs. Similarly, alternative surgical approaches (i.e., cancelloplasty, conservative bone excision, and tibial cortex distraction) have shown early success in limb preservation. Nonoperative strategies, including adjunct antimicrobials, antimicrobial peptides, and topical oxygen, offer additional options, particularly for patients unfit for surgery. While initial outcomes are encouraging, the supporting evidence is heterogeneous and primarily limited to case series and small, noncomparative trials. Overall, these novel therapies show potential as adjuncts to established DFO management, but further prospective research is indicated to define their long-term efficacy, safety, and role in clinical practice.
Keywords: diabetes; diabetic foot; osteomyelitis; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Topical antimicrobial agents for treating foot ulcers in people with diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 14;6(6):CD011038. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011038.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28613416 Free PMC article.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Adjunctive rifampin therapy for diabetic foot osteomyelitis: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 May 29;99(22):e20375. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020375. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32481422 Free PMC article.
-
Growth factors for treating diabetic foot ulcers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Oct 28;2015(10):CD008548. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008548.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26509249 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Qi X., Li Y., Xiang Y., Chen Y., Shi Y., Ge X., Zeng B., Shen J. Hyperthermia-Enhanced Immunoregulation Hydrogel for Oxygenation and ROS Neutralization in Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Cell Biomater. 2025;1:100020. doi: 10.1016/j.celbio.2025.100020. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources