Resveratrol Alleviates Inflammatory Response Through P2X7/NLRP3 Signaling Pathway: In Silico and In Vitro Evidence from Activated Microglia
- PMID: 40732240
- PMCID: PMC12298262
- DOI: 10.3390/ph18070950
Resveratrol Alleviates Inflammatory Response Through P2X7/NLRP3 Signaling Pathway: In Silico and In Vitro Evidence from Activated Microglia
Abstract
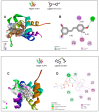
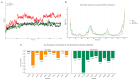
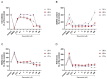
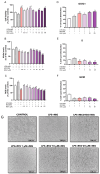
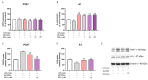
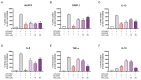
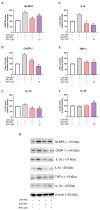
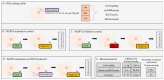
Background/Objectives: Chronic inflammation and inappropriate NLRP3 inflammasome regulation are related to many brain diseases. Purinergic mediators may play an important role in inflammation regulation and could be targeted for effective therapies for these illnesses. We evaluated resveratrol's anti-neuroinflammatory potential in BV-2 microglia cells using an innovative in vitro method of NLRP3 inflammasome activation, correlating with the P2X7 purinergic receptor. Methods: In silico analyses were used to estimate resveratrol's interaction with NLRP3, and its cytotoxicity was measured for 24, 48, and 72 h. Moreover, microglia were exposed to lipopolysaccharide and nigericin to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome and treated with resveratrol between these inflammatory agents. Results: It was found that resveratrol has binding compatible with modulating NLRP3. Specifically, 0.1-25 µM of resveratrol presented a favorable safety profile in BV-2 cells. Microglia exposed to the inflammatory agents had increased levels of oxidative species, the P2X7 receptor, and pro-inflammatory cytokines. However, resveratrol decreased the NLRP3, caspase-1, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α mRNA levels and protein density; on the other hand, IL-10 was increased, acting as a protector, preventing exacerbated inflammation. Under resveratrol exposure, P2X7 was negatively expressed, regulating inflammation to establish homeostasis and microglial proliferation. Additionally, resveratrol activates the A1 adenosine receptor, possibly correlated with neuroprotective effects. Conclusions: We confirmed the anti-neuroinflammatory action of resveratrol via the P2X7 receptor and NLRP3's combined modulation, regulating the cell cycle and reducing pro-inflammatory and oxidant agents. Considering this pathway, resveratrol could be a candidate for further investigations as a potential treatment against neuroinflammatory diseases.
Keywords: BV-2 cells; brain inflammation; immunomodulation; polyphenol; purinergic receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Complement Molecule C3a Exacerbates Early Brain Injury After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage by Inducing Neuroinflammation Through the C3aR-ERK-P2X7-NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling Axis.Inflammation. 2025 Aug;48(4):1791-1810. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02155-7. Epub 2024 Nov 11. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 39528767
-
Resveratrol reduces the activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes in rheumatoid arthritis through SIRT1 and ITGB α5β1, especially in patients with high expression of ACPA.Phytomedicine. 2025 Aug;144:156897. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156897. Epub 2025 May 29. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40480022
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
USP22 inhibits microglial M1 polarization by regulating the PU.1/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway.Brain Res Bull. 2025 Jan;220:111157. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2024.111157. Epub 2024 Dec 2. Brain Res Bull. 2025. PMID: 39631712
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

