Herbal Extract-Induced DNA Damage, Apoptosis, and Antioxidant Effects of C. elegans: A Comparative Study of Mentha longifolia, Scrophularia orientalis, and Echium biebersteinii
- PMID: 40732318
- PMCID: PMC12299367
- DOI: 10.3390/ph18071030
Herbal Extract-Induced DNA Damage, Apoptosis, and Antioxidant Effects of C. elegans: A Comparative Study of Mentha longifolia, Scrophularia orientalis, and Echium biebersteinii
Abstract
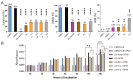
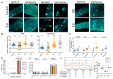
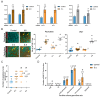
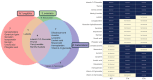
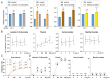
Background: Herbal medicine represents a rich yet complex source of bioactive compounds, offering both therapeutic potential and toxicological risks. Methods: In this study, we systematically evaluated the biological effects of three traditional herbal extracts-Mentha longifolia, Scrophularia orientalis, and Echium biebersteinii-using Caenorhabditis elegans as an in vivo model. Results: All three extracts significantly reduced worm survival, induced larval arrest, and triggered a high incidence of males (HIM) phenotypes, indicative of mitotic failure and meiotic chromosome missegregation. Detailed analysis of germline architecture revealed extract-specific abnormalities, including nuclear disorganization, ectopic crescent-shaped nuclei, altered meiotic progression, and reduced bivalent formation. These defects were accompanied by activation of the DNA damage response, as evidenced by upregulation of checkpoint genes (atm-1, atl-1), increased pCHK-1 foci, and elevated germline apoptosis. LC-MS profiling identified 21 major compounds across the extracts, with four compounds-thymol, carvyl acetate, luteolin-7-O-rutinoside, and menthyl acetate-shared by all three herbs. Among them, thymol and carvyl acetate significantly upregulated DNA damage checkpoint genes and promoted apoptosis, whereas thymol and luteolin-7-O-rutinoside contributed to antioxidant activity. Notably, S. orientalis and E. biebersteinii shared 11 of 14 major constituents (79%), correlating with their similar phenotypic outcomes, while M. longifolia exhibited a more distinct chemical profile, possessing seven unique compounds. Conclusions: These findings highlight the complex biological effects of traditional herbal extracts, demonstrating that both beneficial and harmful outcomes can arise from specific phytochemicals within a mixture. By deconstructing these extracts into their active components, such as thymol, carvyl acetate, and luteolin-7-O-rutinoside, we gain critical insight into the mechanisms driving reproductive toxicity and antioxidant activity. This approach underscores the importance of component-level analysis for accurately assessing the therapeutic value and safety profile of medicinal plants, particularly those used in foods and dietary supplements.
Keywords: DNA repair; Echium biebersteinii; Mentha longifolia; Scrophularia orientalis; germline development; medicinal plants; meiosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
References
-
- Shahar B., Chongtham N. Traditional uses and advances in recent research on wild aromatic plant Mentha longifolia and its pharmacological importance. Phytochem. Rev. 2024;23:529–550. doi: 10.1007/s11101-023-09896-7. - DOI
-
- Jedrzejczyk I., Rewers M. Genome size and ISSR markers for Mentha L. (Lamiaceae) genetic diversity assessment and species identification. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018;120:171–179. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.04.062. - DOI
-
- Galíndez J.d.S., Lanza A.D., Matellano L.F. Biologically Active Substances from the Genus Scrophularia. Pharm. Biol. 2002;40:45–59. doi: 10.1076/phbi.40.1.45.5864. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

