Tumor Niche Influences the Activity and Delivery of Anticancer Drugs: Pharmacology Meets Chemistry
- PMID: 40732334
- PMCID: PMC12298015
- DOI: 10.3390/ph18071047
Tumor Niche Influences the Activity and Delivery of Anticancer Drugs: Pharmacology Meets Chemistry
Abstract
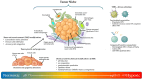
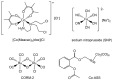
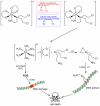
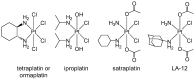
Cellular and molecular characteristics of the tumor microenvironment are fundamental for the formation of niches. These structures include both cellular and matrix components and have been shown to protect and promote cancer formation and progression. The peculiarities of tumor niches have been suggested by many authors as targets with high therapeutic potential. This narrative review analyzes the chemical characteristics of the tumor microenvironment and describes experimental and clinical approaches to influence its contribution to cancer promotion and the spread of metastases. In particular, the possible chemical differences, like pH, oxygen levels, and cell composition, to be used for the design of drugs or the delivery of antiproliferative moieties for a more precise oncology approach, will be discussed. The literature proposes a vast number of molecules, but this review focuses on hypoxia-activated molecules, pH-sensitive nanocarriers, metal-based drugs, and gasotransmitters targeting selectively the tumor microenvironment as possible negative modulators of the contribution of niches to tumor promotion. The chemical peculiarities of the tumor niche are discussed for possible pharmacological developments.
Keywords: hypoxia; metal-based drugs; nanoparticles; pH-sensitive nanocarriers; precise oncology; tumor microenvironment chemistry; tumor niche.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wieke J., Jurcic C., Kaczorowski A., Böning S., Kirchner M., Schwab C., Schütz V., Hohenfellner M., Duensing A., Stenzinger A., et al. Extensive Genotype-Phenotype Heterogeneity in Renal Cell Carcinoma—A Proof-of-Concept Study. Front. Oncol. 2025;15:1551077. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1551077. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

