Toward a User-Accessible Spectroscopic Sensing Platform for Beverage Recognition Through K-Nearest Neighbors Algorithm
- PMID: 40732392
- PMCID: PMC12299580
- DOI: 10.3390/s25144264
Toward a User-Accessible Spectroscopic Sensing Platform for Beverage Recognition Through K-Nearest Neighbors Algorithm
Abstract
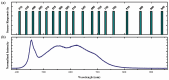
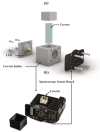
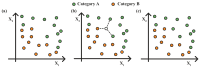
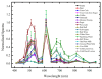
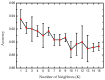
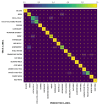
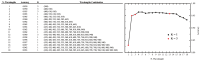
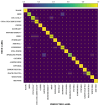
Proper nutrition is a fundamental aspect to maintaining overall health and well-being, influencing both physical and social aspects of human life; an unbalanced or inadequate diet can lead to various nutritional deficiencies and chronic health conditions. In today's fast-paced world, monitoring nutritional intake has become increasingly important, particularly for those with specific dietary needs. While smartphone-based applications using image recognition have simplified food tracking, they still rely heavily on user interaction and raise concerns about practicality and privacy. To address these limitations, this paper proposes a novel, compact spectroscopic sensing platform for automatic beverage recognition. The system utilizes the AS7265x commercial sensor to capture the spectral signature of beverages, combined with a K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) machine learning algorithm for classification. The approach is designed for integration into everyday objects, such as smart glasses or cups, offering a noninvasive and user-friendly alternative to manual tracking. Through optimization of both the sensor configuration and KNN parameters, we identified a reduced set of four wavelengths that achieves over 96% classification accuracy across a diverse range of common beverages. This demonstrates the potential for embedding accurate, low-power, and cost-efficient sensors into Internet of Things (IoT) devices for real-time nutritional monitoring, reducing the need for user input while enhancing accessibility and usability.
Keywords: IoT devices; KNN; beverage recognition; diet monitoring; machine learning; public health; sensing platform; smart cutlery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Khot R.A., Mueller F. Human-Food Interaction. Found. Trends® Hum.–Comput. Interact. 2019;12:238–415. doi: 10.1561/1100000074. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

