A Systematic Review of Cyber Threat Intelligence: The Effectiveness of Technologies, Strategies, and Collaborations in Combating Modern Threats
- PMID: 40732398
- PMCID: PMC12300000
- DOI: 10.3390/s25144272
A Systematic Review of Cyber Threat Intelligence: The Effectiveness of Technologies, Strategies, and Collaborations in Combating Modern Threats
Abstract
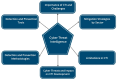
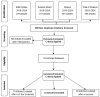
Cyber threat intelligence (CTI) has become critical in enhancing cybersecurity measures across various sectors. This systematic review aims to synthesize the current literature on the effectiveness of CTI strategies in mitigating cyber attacks, identify the most effective tools and methodologies for threat detection and prevention, and highlight the limitations of current approaches. An extensive search of academic databases was conducted following the PRISMA guidelines, including 43 relevant studies. This number reflects a rigorous selection process based on defined inclusion, exclusion, and quality criteria and is consistent with the scope of similar systematic reviews in the field of cyber threat intelligence. This review concludes that while CTI significantly improves the ability to predict and prevent cyber threats, challenges such as data standardization, privacy concerns, and trust between organizations persist. It also underscores the necessity of continuously improving CTI practices by leveraging the integration of advanced technologies and creating enhanced collaboration frameworks. These advancements are essential for developing a robust and adaptive cybersecurity posture capable of responding to an evolving threat landscape, ultimately contributing to a more secure digital environment for all sectors. Overall, the review provides practical reflections on the current state of CTI and suggests future research directions to strengthen and improve CTI's effectiveness.
Keywords: AI; advanced persistent threats; cyber threat intelligence; cybersecurity; frameworks; machine learning; platforms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Buczak A.L., Guven E. A Survey of Data Mining and Machine Learning Methods for Cyber Security Intrusion Detection. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016;18:1153–1176. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2015.2494502. - DOI
-
- Salah K., Rehman M.H.U., Nizamuddin N., Al-Fuqaha A. Blockchain for AI: Review and Open Research Challenges. IEEE Access. 2019;7:10127–10149. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2890507. - DOI
-
- Tounsi W., Rais H. A survey on technical threat intelligence in the age of sophisticated cyber attacks. Comput. Secur. 2018;72:212–233. doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2017.09.001. - DOI
-
- Chatziamanetoglou D., Rantos K. Cyber Threat Intelligence on Blockchain: A Systematic Literature Review. Computers. 2024;13:60. doi: 10.3390/computers13030060. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources