Autonomous Waste Classification Using Multi-Agent Systems and Blockchain: A Low-Cost Intelligent Approach
- PMID: 40732493
- PMCID: PMC12300469
- DOI: 10.3390/s25144364
Autonomous Waste Classification Using Multi-Agent Systems and Blockchain: A Low-Cost Intelligent Approach
Abstract
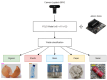
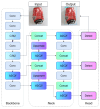
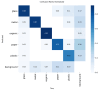
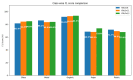
The increase in garbage generated in modern societies demands the implementation of a more sustainable model as well as new methods for efficient waste management. This article describes the development and implementation of a prototype of a smart bin that automatically sorts waste using a multi-agent system and blockchain integration. The proposed system has sensors that identify the type of waste (organic, plastic, paper, etc.) and uses collaborative intelligent agents to make instant sorting decisions. Blockchain has been implemented as a technology for the immutable and transparent control of waste registration, favoring traceability during the classification process, providing sustainability to the process, and making the audit of data in smart urban environments transparent. For the computer vision algorithm, three versions of YOLO (YOLOv8, YOLOv11, and YOLOv12) were used and evaluated with respect to their performance in automatic detection and classification of waste. The YOLOv12 version was selected due to its overall performance, which is superior to others with mAP@50 values of 86.2%, an overall accuracy of 84.6%, and an average F1 score of 80.1%. Latency was kept below 9 ms per image with YOLOv12, ensuring smooth and lag-free processing, even for utilitarian embedded systems. This allows for efficient deployment in near-real-time applications where speed and immediate response are crucial. These results confirm the viability of the system in both accuracy and computational efficiency. This work provides an innovative solution in the field of ambient intelligence, characterized by low equipment cost and high scalability, laying the foundations for the development of smart waste management infrastructures in sustainable cities.
Keywords: blockchain; intelligent classification; multi-agent systems; smart waste management.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures













Similar articles
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Wood Waste Valorization and Classification Approaches: A systematic review.Open Res Eur. 2025 May 6;5:5. doi: 10.12688/openreseurope.18862.2. eCollection 2025. Open Res Eur. 2025. PMID: 40438563 Free PMC article.
-
Designing A Blockchain-Empowered Telehealth Artifact for Decentralized Identity Management and Trustworthy Communication: Interdisciplinary Approach.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Sep 25;26:e46556. doi: 10.2196/46556. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39320943 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wowrzeczka B. City of Waste—Importance of Scale. Sustainability. 2021;13:3909. doi: 10.3390/su13073909. - DOI
-
- Valentin A.P.M., Bonifacio P.B.S.D., Castro S.I.C.O., Ruiz J.C.A., Sy T.I.L., Trinidad E.L.O. Predicting Waste Management Behaviors Using an Extended Theory of Reasoned Action Model. Clean. Waste Syst. 2024;9:100193. doi: 10.1016/j.clwas.2024.100193. - DOI
-
- Bueno-Suárez C., Coq-Huelva D. Sustaining What Is Unsustainable: A Review of Urban Sprawl and Urban Socio-Environmental Policies in North America and Western Europe. Sustainability. 2020;12:4445. doi: 10.3390/su12114445. - DOI
-
- Campos-Alba C.M., Garrido-Rodríguez J.C., Plata-Díaz A.M., Pérez-López G. The Selective Collection of Municipal Solid Waste and Other Factors Determining Cost Efficiency: An Analysis of Service Provision by Spanish Municipalities. Waste Manag. 2021;119:11–20. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2021.07.039. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahmadi M., Karbassi A.R., Amrane A. A review of soil pollution around municipal solid waste landfills in Iran and comparable instances from other parts of the world. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024;21:4567–4585. doi: 10.1007/s13762-024-05728-z. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

