Evaluating Polylactic Acid and Basalt Fibre Composites as a Potential Bioabsorbable Stent Material
- PMID: 40732827
- PMCID: PMC12298794
- DOI: 10.3390/polym17141948
Evaluating Polylactic Acid and Basalt Fibre Composites as a Potential Bioabsorbable Stent Material
Abstract
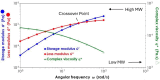
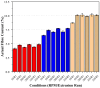
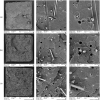
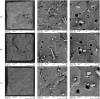
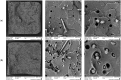
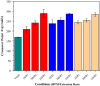
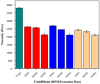
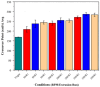
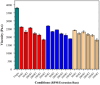
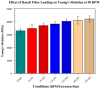
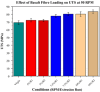
Bioabsorbable polymer stents (BPSs) were developed to address the long-term clinical drawbacks associated with permanent metallic stents by gradually dissolving over time before these drawbacks have time to develop. However, the polymers used in BPSs, such as polylactic acid (PLA), have lower mechanical properties than metals, often requiring larger struts to provide the necessary structural support. These larger struts have been linked to delayed endothelialisation and an increased risk of stent thrombosis. To address this limitation, this study investigated the incorporation of high-strength basalt fibres into PLA to enhance its mechanical performance, with an emphasis on optimising the processing conditions to achieve notable improvements at minimal fibre loadings. In this regard, PLA/basalt fibre composites were prepared via twin-screw extrusion at screw speeds of 50, 200, and 350 RPM. The effects were assessed through ash content testing, tensile testing, SEM, and rheometry. The results showed that lower screw speeds achieved adequate fibre dispersion while minimising the molecular weight reduction, leading to the most substantial improvement in the mechanical properties. To examine whether a second extrusion run could enhance the fibre dispersion, improving the composite's uniformity and, therefore, mechanical enhancement, all the batches underwent a second extrusion run. This run improved the dispersion, leading to increased strength and an increased modulus; however, it also reduced the fibre-matrix adhesion and resulted in a notable reduction in the molecular weight. The highest mechanical performance was observed at 10% fibre loading and 50 RPM following a second extrusion run, with the tensile strength increasing by 20.23% and the modulus by 27.52%. This study demonstrates that the processing conditions can influence the fibres' effectiveness, impacting dispersion, adhesion, and molecular weight retention, all of which affect this composite's mechanical performance.
Keywords: basalt fibre; bioabsorbable polymer stents; polylactic acid; twin-screw extrusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Franchin L., Piroli F., D’Ascenzo F., Nuñez-Gil I., Wojakowski W., Imori Y., Trabattoni D., Huczek Z., Venuti G., Muscoli S., et al. Impact of stent thickness on clinical outcomes in small vessel and bifurcation lesions: A RAIN-CARDIOGROUP VII sub-study. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021;22:20–25. doi: 10.2459/JCM.0000000000001037. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

