A Systematic Review of Epoxidation Methods and Mechanical Properties of Sustainable Bio-Based Epoxy Resins
- PMID: 40732835
- PMCID: PMC12299802
- DOI: 10.3390/polym17141956
A Systematic Review of Epoxidation Methods and Mechanical Properties of Sustainable Bio-Based Epoxy Resins
Abstract
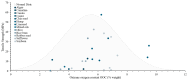
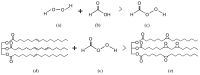
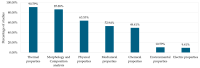
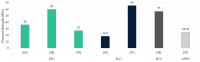
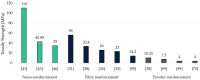
There has been a growing interest in polymer-based materials in recent years, and current research is focused on reducing fossil-derived epoxy compounds. This review examines the potential of epoxidised vegetable oils (EVOs) as sustainable alternatives to these systems. Epoxidation processes have been systematically analysed and their influence on chemical, thermal, and mechanical properties has been assessed. Results indicate that basic, low-toxicity epoxidation methods resulted in resins with comparable performance to those obtained through more complex common/commercial procedures. In total, 5-7% oxirane oxygen content (OOC) was found to be optimal to achieve a balanced crosslink density, thus enhancing tensile strength. Furthermore, mechanical properties have been insufficiently studied, as less than half of the studies were conducted at least tensile or flexural strength. Reinforcement strategies were also explored, with nano-reinforcing carbon nanotubes (CBNTs) showing the best mechanical and thermal results. Natural fibres reported better mechanical performance when mixed with EVOs than conventional systems. On the other hand, one of the main constraints observed is the lack of consistency in reporting key chemical and mechanical parameters across studies. Environmental properties and end-of-life use are significant challenges to be addressed in future studies, as there remains a significant gap in understanding the end-of-life of these materials. Future research should focus on the exploration of eco-friendly epoxidation reagents and standardise protocols to compare and measure oil properties before and after being epoxidised.
Keywords: epoxidation process; epoxidised vegetable oils; mechanical properties; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




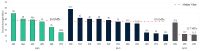

References
-
- da Silva Costa D., de Novais L.M.R., D’OCa C.D.R.M., Marques J.F., Ferreira C.A., Mazzetto S.E., Lomonaco D., Avelino F. Towards phosphorylated lignin-based epoxy resins: An integrated technological route to obtain a macromonomer with enhanced thermal and potential flame-retardant properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025;304:140821. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140821. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change . Climate Change 2023 Synthesis Report. IPCC; Geneva, Switzerland: 2023. - DOI
-
- Yin R., Liu Y., Luo Y., Yan J., Li J., Chen D., Sun T., Li S., Wu Z. Enhancing the liquid oxygen compatibility of epoxy resin by introducing a novel phosphorus/sulfur-containing flame retardant. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2025;236:111296. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2025.111296. - DOI
-
- Hanif M., Zahoor A.F., Saif M.J., Nazeer U., Ali K.G., Parveen B., Mansha A., Chaudhry A.R., Irfan A. Exploring the synthetic potential of epoxide ring opening reactions toward the synthesis of alkaloids and terpenoids: A review. RSC Adv. 2024;14:13100–13128. doi: 10.1039/D4RA01834F. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saravanamuthu S.K.S., Mahendran A.R., Wuzella G., Weiss S., Schöffmann E. Investigation of the formation of epoxy-imidazole adducts and the kinetic triplets during thermal curing of a biobased and petrochemical epoxy with anhydride. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2024;149:11025–11039. doi: 10.1007/s10973-024-13415-x. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

