Single-Gelator Structuring of Hemp Oil Using Agarose: Comparative Assembly, Electronic Nose Profiling, and Functional Performance of Hydroleogels Versus Oleogels in Shortbread Cookies
- PMID: 40732866
- PMCID: PMC12300686
- DOI: 10.3390/polym17141988
Single-Gelator Structuring of Hemp Oil Using Agarose: Comparative Assembly, Electronic Nose Profiling, and Functional Performance of Hydroleogels Versus Oleogels in Shortbread Cookies
Abstract
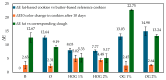
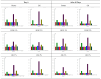
This study demonstrates an innovative single-gelator approach using agarose (1% and 2% w/w) to structure cold-pressed hemp oil into functional fat replacers for shortbread cookies, achieving a 40% reduction in saturated fatty acids compared to butter. Comprehensive characterization revealed that hydroleogels exhibited superior crispiness (45.67 ± 3.86 N for 2% agarose hydroleogel-HOG 2%) but problematic water activity (0.39-0.61), approaching microbial growth thresholds. Conversely, oleogels showed lower crispiness (2.27-3.43 N) but optimal moisture control (aw = 0.12-0.16) and superior color stability during 10-day storage. Electronic nose analysis using 10 metal oxide sensors revealed that oleogel systems preserved characteristic aroma profiles significantly better than hydroleogels, with 2% agarose oleogel (OG 2%) showing 34% less aroma decay than pure hemp oil. The 2% agarose oleogel demonstrated optimal performance with minimal baking loss (5.87 ± 0.20%), excellent structural integrity, and stable volatile compound retention over storage. Morphological analysis showed that hemp oil cookies achieved the highest specific volume (2.22 ± 0.07 cm3/g), while structured systems ranged from 1.12 to 1.31 cm3/g. This work establishes agarose as a versatile single gelator for hemp oil structuring and validates electronic nose technology for the objective quality assessment of fat-replaced bakery products, advancing healthier food design through molecular approaches.
Keywords: agarose; electronic nose; fat replacement; hemp oil; hydroleogel; oleogel; shortbread; texture; water activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Paciulli M., Littardi P., Carini E., Paradiso V.M., Castellino M., Chiavaro E. Inulin-Based Emulsion Filled Gel as Fat Replacer in Shortbread Cookies: Effects during Storage. LWT. 2020;133:109888. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109888. - DOI
-
- European Parliament Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 on Nutrition and Health Claims Made on Foods. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2006;L404:9–25.
-
- Giarnetti M., Paradiso V.M., Caponio F., Summo C., Pasqualone A. Fat Replacement in Shortbread Cookies Using an Emulsion Filled Gel Based on Inulin and Extra Virgin Olive Oil. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2015;63:339–345. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2015.03.063. - DOI
-
- Marangoni A., Garti N. Edible Oleogels: Structure and Health Implications. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2011. pp. 70–120.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

