Key Aspects in the Nutritional Management of Polycystic Liver Disease Patients
- PMID: 40733005
- PMCID: PMC12299131
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17142380
Key Aspects in the Nutritional Management of Polycystic Liver Disease Patients
Abstract
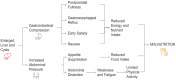
Polycystic liver disease (PLD) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the development of >10 fluid-filled cysts in the liver. While PLD can occur in isolation, it is most commonly associated with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, adding complexity to its management. PLD is often asymptomatic but can lead to hepatomegaly, causing symptoms such as abdominal distension, pain and discomfort, early satiety, gastroesophageal reflux, and malnutrition, ultimately affecting patients' quality of life. Current treatment strategies, including pharmacological and interventional approaches, focus on reducing liver volume and alleviating symptoms. However, management remains largely symptomatic, as no definitive therapies exist to halt cyst progression. Liver transplantation is the only curative option for patients with severe, progressive disease and refractory complications. The EASL guidelines recognize that PLD-related symptoms, primarily due to hepatomegaly, can contribute to involuntary weight loss and recommend assessing symptomatic patients for malnutrition and sarcopenia. Although evidence suggests that patients with PLD may be at risk of malnutrition, original data on the quality and extent of nutritional alterations remain scarce. The potential influence of nutrition on disease progression, symptom burden, and overall well-being is also largely unexplored. Given these knowledge gaps, addressing nutritional challenges, such as early satiety, is essential for optimizing symptom management and maintaining overall nutritional status. This review outlines a possible pathophysiology of malnutrition, specific dietary considerations and recommendations, and weight management in patients with PLD. Additionally, dietary complexities in patients with concurrent renal involvement are discussed, offering a practical framework for clinicians and dietitians in managing this challenging condition.
Keywords: malnutrition; nutrition; polycystic liver disease; quality of life; sarcopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multidisciplinary collaborative guidance on the assessment and treatment of patients with Long COVID: A compendium statement.PM R. 2025 Jun;17(6):684-708. doi: 10.1002/pmrj.13397. Epub 2025 Apr 22. PM R. 2025. PMID: 40261198
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Oral nutritional interventions in frail older people who are malnourished or at risk of malnutrition: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Dec;26(51):1-112. doi: 10.3310/CCQF1608. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 36541454 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Citrullinemia Type I.2004 Jul 7 [updated 2022 Aug 18]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. 2004 Jul 7 [updated 2022 Aug 18]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. PMID: 20301631 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
-
- Torres V.E., Ahn C., Barten T.R.M., Brosnahan G., Cadnapaphornchai M.A., Chapman A.B., Gall E.C.-L., Drenth J.P.H., Gansevoort R.T., Harris P.C., et al. KDIGO 2025 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation, Management, and Treatment of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD): Executive Summary. Kidney Int. 2025;107:234–254. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2024.07.010. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical