Endo/Lysosomal-Escapable Lipid Nanoparticle Platforms for Enhancing mRNA Delivery in Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 40733013
- PMCID: PMC12300936
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17070803
Endo/Lysosomal-Escapable Lipid Nanoparticle Platforms for Enhancing mRNA Delivery in Cancer Therapy
Abstract
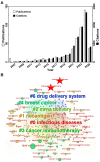
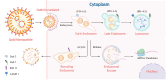
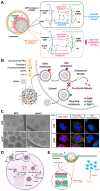
mRNA-based drug development is revolutionizing tumor therapies by enabling precise cancer immunotherapy, tumor suppressor gene restoration, and genome editing. However, the success of mRNA therapies hinges on efficient delivery systems that can protect mRNA from degradation and facilitate its release into the cytoplasm for translation. Despite the emergence of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) as a clinically advanced platform for mRNA delivery, the efficiency of endo/lysosomal escape still represents a substantial bottleneck. Here, we summarize the intracellular fate of mRNA-loaded LNPs, focusing on their internalization pathways and processing within the endo-lysosomal system. We also discuss the impact of endo-lysosomal processes on mRNA delivery and explore potential strategies to improve mRNA escape from endo-lysosomal compartments. This review focuses on molecular engineering strategies to enhance LNP-mediated endo/lysosomal escape by optimizing lipid composition, including ionizable lipids, helper lipids, cholesterol, and PEGylated lipids. Additionally, ancillary enhancement strategies such as surface coating and shape management are discussed. By comprehensively integrating mechanistic insights into the journey of LNPs within the endo-lysosome system and recent advances in lipid chemistry, this review offers valuable inspiration for advancing mRNA-based cancer therapies by enabling robust protein expression.
Keywords: endo/lysosomal escape; gene therapy; lipid nanoparticle; mRNA delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

