Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from Enicostemma littorale Exhibit Gut Tight Junction Restoration and Hepatoprotective Activity via Regulation of the Inflammatory Pathway
- PMID: 40733103
- PMCID: PMC12298411
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17070895
Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from Enicostemma littorale Exhibit Gut Tight Junction Restoration and Hepatoprotective Activity via Regulation of the Inflammatory Pathway
Abstract
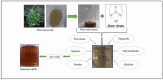
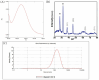
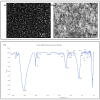
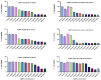
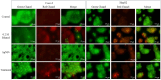
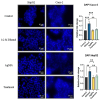
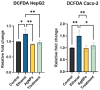
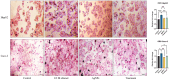
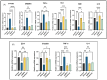
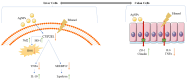
Background: Alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) is a primary global health concern, exacerbated by oxidative stress, inflammation, and gut barrier dysfunction. Conventional phytocompounds exhibit hepatoprotective potential but are hindered by low bioavailability. This study aimed to evaluate the hepatoprotective and gut-barrier-restorative effects of green-synthesized silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) derived from Enicostemma littorale, a medicinal plant known for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Methods: AgNPs were synthesized using aqueous leaf extract of E. littorale and characterized using UV-Vis, XRD, FTIR, DLS, and SEM. HepG2 (liver) and Caco-2 (colon) cells were exposed to 0.2 M ethanol, AgNPs (1-100 µg/mL), or both, to simulate ethanol-induced toxicity. A range of in vitro assays was performed to assess cell viability, oxidative stress (H2DCFDA), nuclear and morphological integrity (DAPI and AO/EtBr staining), lipid accumulation (Oil Red O), and gene expression of pro- and anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and tight-junction markers using RT-qPCR. Results: Ethanol exposure significantly increased ROS, lipid accumulation, and the expression of inflammatory genes, while decreasing antioxidant enzymes and tight-junction proteins. Green AgNPs at lower concentrations (1 and 10 µg/mL) restored cell viability, reduced ROS levels, preserved nuclear morphology, and downregulated CYP2E1 and SREBP expression. Notably, AgNPs improved the expression of Nrf2, HO-1, ZO-1, and IL-10, and reduced TNF-α and IL-6 expression in both cell lines, indicating protective effects on both liver and intestinal cells. Conclusions: Green-synthesized AgNPs from E. littorale exhibit potent hepatoprotective and gut-barrier-restoring effects through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antilipidemic mechanisms. These findings support the therapeutic potential of plant-based nanoparticles in mitigating ethanol-induced gut-liver axis dysfunction.
Keywords: AgNPs; Enicostemma littorale dried leaves; alcohol-associated liver disease; green synthesis; gut barrier; hepatoprotective activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yaqub A., Ditta S.A., Anjum K.M., Tanvir F., Malkani N., Yousaf M.Z. Comparative Analysis of Toxicity Induced by Different Synthetic Silver Nanoparticles in Albino Mice. BioNanoScience. 2019;9:553–563. doi: 10.1007/s12668-019-00642-y. - DOI
-
- Javed S., Kohli K., Ahsan W. Bioavailability augmentation of silymarin using natural bioenhancers: An in vivo pharmacokinetic study. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022;58:e20160. doi: 10.1590/s2175-97902022e20160. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

