Trends and Commonalities of Approved and Late Clinical-Phase RNA Therapeutics
- PMID: 40733111
- PMCID: PMC12300435
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17070903
Trends and Commonalities of Approved and Late Clinical-Phase RNA Therapeutics
Abstract
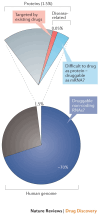
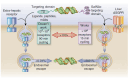
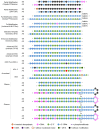
Background/Objectives: After many years of research and the successful development of therapeutic products by a few industrial actors, the COVID-19 vaccines brought messenger RNAs, as well as other nucleic acid modalities, such as antisense oligonucleotides, small interfering RNA, and aptamers, into the spotlight, eliciting renewed interest from both academia and industry. However, owing to their structure, relative "fragility", and the (usually) intracellular site of action, the delivery of these therapeutics has frequently proven to be a key limitation, especially when considering endosomal escape, which still needs to be overcome. Methods: By compiling delivery-related data on approved and late clinical-phase ribonucleic acid therapeutics, this review aims to assess the delivery strategies that have proven to be successful or are emerging, as well as areas where more research is needed. Results: In very specific cases, some strategies appeared to be quite effective, such as the N-acetylgalactosamine moiety in the case of liver delivery. Surprisingly, it also appears that for some modalities, efforts in molecular design have led to more "drug-like" properties, enablingthe administration of naked nucleic acids, without any form of encapsulation. This appears to be especially true when local administration, i.e., by injection, is possible, as this provides de facto targeting and a high local concentration, which can compensate for the small proportion of nucleic acids that reach the cytoplasm. Conclusions: Nucleic acid-based therapeutics have come a long way in terms of their physicochemical properties. However, due to their inherent limitations, targeting appears to be crucial for their efficacy, even more so than for traditional pharmaceutical modalities.
Keywords: delivery; endosomal escape; local administration; nucleic acids; targeting; topical.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
References
-
- Newey S. ‘No Limits’ to Possibilities of MRNA, Says Mastermind behind Technology. The Telegraph. Dec 29, 2022.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

