Functional Role of Resveratrol in Inducing Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Subtypes via Inhibition of Intracellular Fatty Acid Synthase
- PMID: 40733158
- PMCID: PMC12298780
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30142891
Functional Role of Resveratrol in Inducing Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Subtypes via Inhibition of Intracellular Fatty Acid Synthase
Abstract
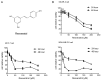
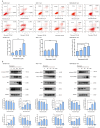
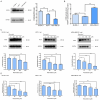
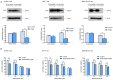
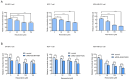
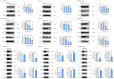
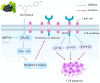
Fatty acid synthase (FASN) is frequently overexpressed in human breast cancer and has emerged as a potential therapeutic target. Resveratrol has been shown to inhibit FASN activity in vitro through both fast-reversible and slow-irreversible mechanisms. In this study, resveratrol reduced intracellular fatty acid levels by inhibiting FASN activity and downregulating its expression across various breast cancer subtypes, including SK-BR-3, MCF-7, and MDA-MB-231 cells. Knockdown of FASN via small interfering RNA (siRNA) further enhanced resveratrol-induced cytotoxicity. Resveratrol significantly suppressed cell viability and triggered apoptosis, as evidenced by increased cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) and disruption of Bcl-2 family protein balance. Furthermore, resveratrol inhibited key signaling pathways involved in cell proliferation and survival, notably FAK, AKT, and ERK1/2. FASN silencing by siRNA also modulated the activation states of these signaling proteins. Collectively, these findings support resveratrol as a promising anti-cancer candidate that induces apoptosis in diverse breast cancer subtypes via FASN inhibition.
Keywords: breast cancer cells; cell apoptosis; fatty acid synthase; inhibitor; resveratrol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

