Chirality Transfer and Oxazolidine Formation in Reaction of L and D Enantiomers of β-Hydroxy Amino Acids with Nitrogenous Carboxaldehydes and Nickel(II)
- PMID: 40733184
- PMCID: PMC12298519
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30142913
Chirality Transfer and Oxazolidine Formation in Reaction of L and D Enantiomers of β-Hydroxy Amino Acids with Nitrogenous Carboxaldehydes and Nickel(II)
Abstract
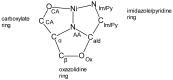
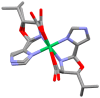
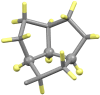
The reaction of either the L (2S3R) or D (2R3S) enantiomers of H2N-C*H(R)CO2- (R = -C*H(OH)CH3 or -C*H(OH)CH(CH3)2) and the L (2S) or D (2R) enantiomers of H2N-C*H(C(CH3)2OH)CO2- with imidazole-4-carboxaldehyde and nickel(II) acetate in methanol yields a single stereoisomer of an oxazolidine. There is retention of chirality on ring positions 4 and 5 (if Cβ is chiral) of the oxazolidine, Cα and Cβ of the parent amino acid, and transfer of chirality to the newly generated stereogenic centers, ring positions 3, the amino acid nitrogen atom, NAA, and 2, the aldehyde carbon atom, Cald. Specifically, when Cα has an S configuration, both NAA and Cald are formed as R. Likewise, a Cα which is R results in both NAA and Cald being formed as S. For example, the reaction of L threonine (Cα is S and Cβ is R) with 4-imidazolecarboxaldehyde in the presence of nickel(II) gives the facial Λ NiL2, where L is (2R, 3R, 4S, 5R) 4-carboxylato-5-methyl-2-(4-imidazolyl)-1,3-oxazolidine. The same reaction with D threonine produces the enantiomeric Δ complex of (2S, 3S, 4R, 5S) 4-carboxylato-5-methyl-2-(4-imidazoyl)-1,3-oxazolidine. The high stereospecificity is thought to be based on the fused three-ring structure of the characterized nickel complexes in which the hydrogen atoms of Cα, NAA, and Cald must be cis to one another. Identical reactions occur with 2-pyridine carboxaldehyde and LT or DT. In contrast, the reactions of L allo threonine (2S3S) and the primary alcohols, L or D serine, give the conventional meridionally coordinated aldimine product.
Keywords: beta hydroxy amino acids; chirality transfer; homochirality; oxazolidine; threonine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



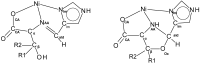


Similar articles
-
Sickle Cell Disease.2003 Sep 15 [updated 2025 Feb 13]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. 2003 Sep 15 [updated 2025 Feb 13]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. PMID: 20301551 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Citrullinemia Type I.2004 Jul 7 [updated 2022 Aug 18]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. 2004 Jul 7 [updated 2022 Aug 18]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. PMID: 20301631 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
-
- Pichon-Barre D., Zhang Z., Cador A., Vives T., Roisnel T., Basle O., Jarrige L., Cavallo L., Falivene L., Mauduit M. Chiral oxazolidines acting as transientlhydroxy-alkyl-functionalized N-heterocyclic carbenes: An efficient route to gold and copper complexes for asymmetric catalysis. Chem. Sci. 2022;13:8773–8780. doi: 10.1039/D2SC02908A. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ng C.-H., Wang W.-S., Chong K.-V., Win Y.-F., Neo K.-E., Lee H.-B., San S.-L., Rahman R., Leong W. Ternary copper(II)-polypyridyl enantiomers: Aldol-type condensation, characterization, DNA-binding recognition, BSA-binding and anticancer property. Dalton Trans. 2013;42:10233–10243. doi: 10.1039/c3dt50884f. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lee K., Ng Y., Wang W., Ng P., Chan C., Lai J., Davamani F., Chitra E., Lim W., Ganguly R., et al. Enantiomeric pairs of ternary copper(ii) complexes and their aldol-type condensation products: Synthesis, characterization, and anticancer and epigenetic properties. Dalton Trans. 2019;48:4987–4999. doi: 10.1039/C9DT00506D. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

